Test: Magnetic Effects of Electric Current - Class 10 MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
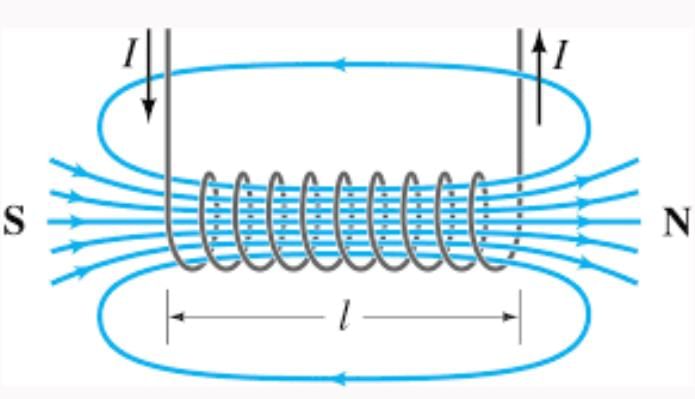
The magnetic field lines inside a long current-carrying solenoid are near-
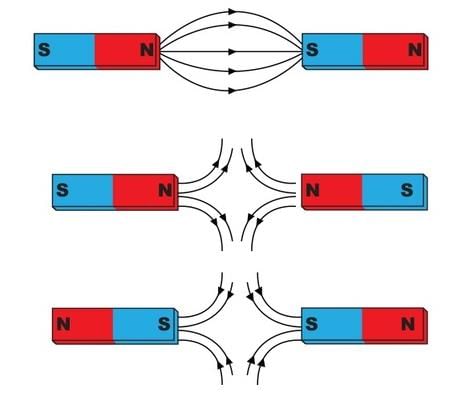
Moving two like poles together usually causes a magnet resting on a table to repel and rotate. This occurs because:
An electric current flowing through a conductor produces
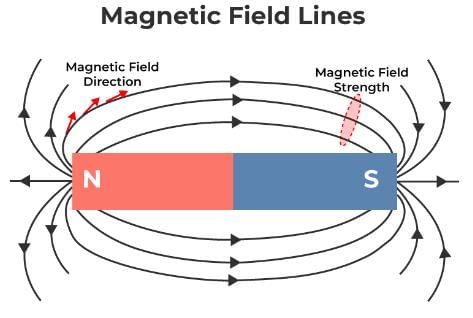
Magnetic lines of force originate from the
A magnetic field existing around a magnet can be represented by magnetic field lines. Magnetic field lines always form:
Which of the following statement concerning magnetic field is correct ?
(1) The part of a bar magnet, at which the magnetic field is the strongest, is called its pole.
(2) A magnetic field is present near a compass needle.
(3) There is no magnetic field inside a current-carrying solenoid.
A vertical wire carries a current straight down. To the east of this wire, the magnetic field points:
Which of the following metal is not attracted by a magnet ?
In which direction does a freely suspended compass needle align itself ?