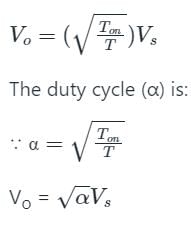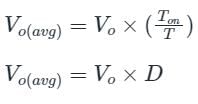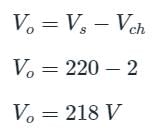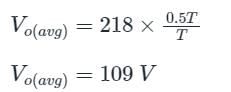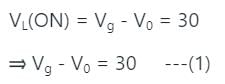Test: Step Down Choppers - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Step Down Choppers
A buck converter has an input current of 2.4 A while required output current is 6 A. What will be the duty cycle of the converter? [Assume lossless system]
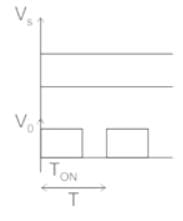
Average output voltage of a step-down chopper with TON = 0.2s and TOFF = 0.3s, if the supply voltage is 15 V, is given by:
A buck converter is used to control a d.c. motor. The input to a dc buck converter is 200 V. Find the duty ratio of the pulse to be applied to the converter to produce 150 V across the d.c. motor.
A DC-DC buck converter operates in continuous conduction mode. It has 48 V input voltage, and it feeds a resistive load of 24 Ω. The switching frequency of the converter is 250 Hz. If switch-on duration is 1 ms, the load power is
The duty cycle of a step-down chopper is 55% and the value of the source voltage is 100 V. Find its output voltage.
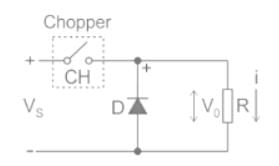
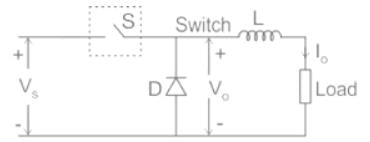
A step-down chopper operates from a DC voltage source Vs and feeds a DC motor armature with counter emf Eb. From oscilloscope traces it is found that current increases for time tr, falls to zero over a time tf and remains zero for a time t0 in every chopping cycle. Then the average voltage across the motor would be
For a step-down DC chopper with a resistive load, when the duty cycle is increased the average value of the output voltage-
A step-down chopper has Vs as a source voltage, α is the duty ratio and R is the load resistance. The r.m.s. value of output voltage is
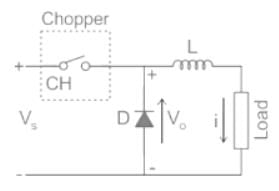
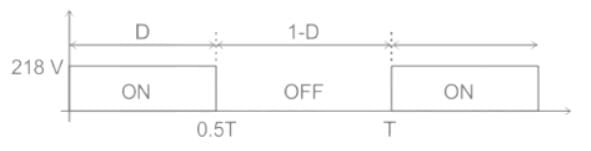
A DC chopper has a resistive load of R = 10 Ω and an input voltage of Vs = 220 V. When the chopper switch remains in the ON state, its voltage drop is Vch = 2 V. If the duty cycle is 50%, determine its average output voltage Vo.
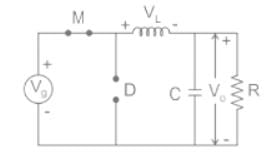
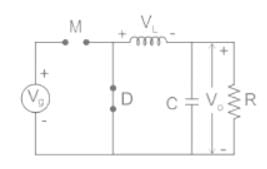
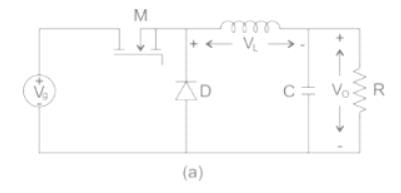
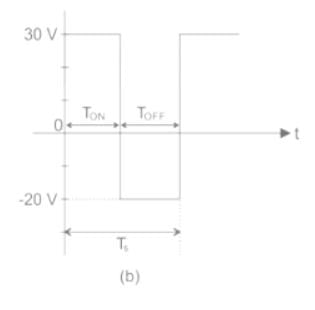
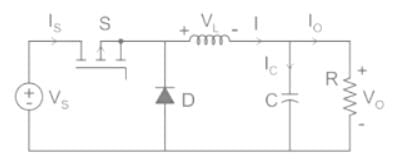
A buck converter, as shown in Figure (a) below, is working in steady state. The output voltage and the inductor current can be assumed to be ripple free. Figure (b) shows the inductor voltage VL during a complete switching interval. Assuming all devices are ideal, the duty cycle of the buck converter is ________.


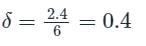
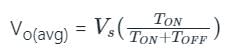


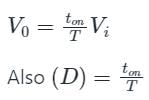
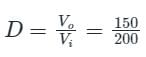
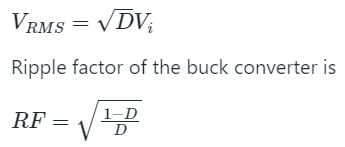
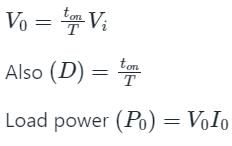
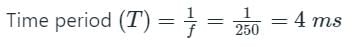
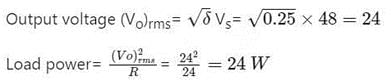
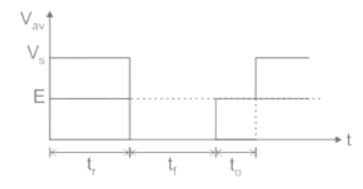
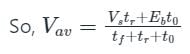
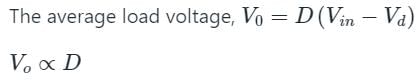
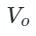 also increases.
also increases.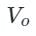 is the average load voltage.
is the average load voltage.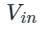 is the input voltage.
is the input voltage.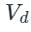 is the voltage drop across the switch in the ON condition.
is the voltage drop across the switch in the ON condition.