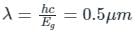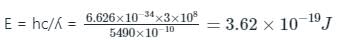Test: Direct & Indirect Band Gap Semiconductors - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) MCQ
6 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Direct & Indirect Band Gap Semiconductors
Silicon is not suitable for fabrication of light emitting diodes because it is:
Direction: Question consists of two statements, one labeled as the 'Assertion (A)' and the other as 'Reason (R)'. Examine these two statements carefully and select the answer to this question using the codes given below:
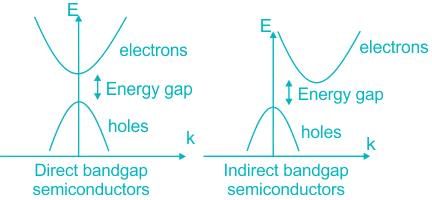
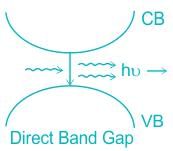
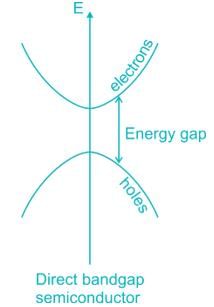
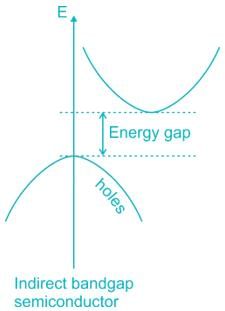
Assertion (A): Many semiconductors where minimum energy in the conduction band and maximum energy in the valence band occur at the same value of 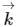 (wave vector), are preferred for optical lenses.
(wave vector), are preferred for optical lenses.
Reason (R): For such semiconductors, the efficiency of carrier generation and recombination is very high.
Assertion (A): Many semiconductors where minimum energy in the conduction band and maximum energy in the valence band occur at the same value of
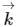 (wave vector), are preferred for optical lenses.
(wave vector), are preferred for optical lenses.Reason (R): For such semiconductors, the efficiency of carrier generation and recombination is very high.
Which of the following is used to make Light Emitting Diodes (LED)?
If one makes an LED in a semiconductor with a direct bandgap of 2.5eV, the wavelength of light emitted will be ________μm. (Given, Planck’s constant is 6.626x10-34 J-s and velocity of light is 3x108 m/s)
Which of the following is the best photo sensitive material?
A particular green LED emits light of wavelength 5490ºA. The energy band gap of the semiconductor material used there is (Planck’s constant = 6.626×10-34 J-s)