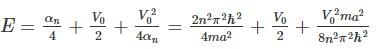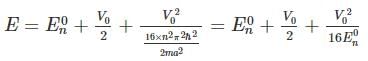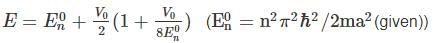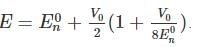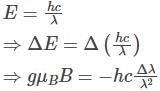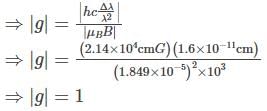CSIR NET Physical Science Mock Test - 1 - UGC NET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - CSIR NET Physical Science Mock Test - 1
A five digit number is formed with the digit 1,2,3,4 and 5 without repetition. Find the chance that the number is divisible by 5 ?
If ‘S – T’ means ‘S is the wife of T’; ‘S + T’ means ‘S is the daughter of T’ and ‘S ÷ T’ means ‘S is the son of T’. What will ‘M + J ÷ K’ means?
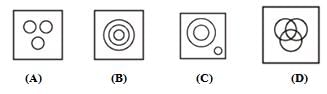
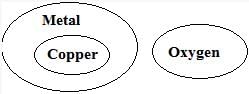
Direction: Identify the diagram that best represents the relationship between the given classes.
Metal, Oxygen, Copper

Let S = [0, 1] ∪ [2, 3) and let f : S → R be defined by
If T = {f(x) : x ∈ S}, then the inverse function f–1 : T → S
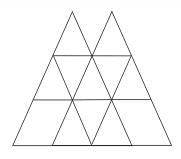
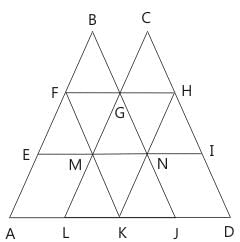
find the number of triangles in the given figure.
Directions: Study the given table carefully and answer the question that follow:
Number of candidates appeared and qualified for a test (in hundreds) in 6 different years from 5 different zones.
Note: Here App. means Appeared and Qual. Means qualified.

Q. From which zone was the total number of candidates who qualified the test, the second highest in the year 2009 and 2010?
PQRS is a circle and circles are drawn with PO, QO, RO and SO as diameters. Areas A and B are marked. A/B is equal to:
A Sales Executive gets a commission on total sales at 8%. If the sale is exceeded Rs.10,000 he gets an additional commission as a bonus of 4% on the excess of sales over Rs.10,000. If he gets the total commission of Rs.950, then the bonus he received is?
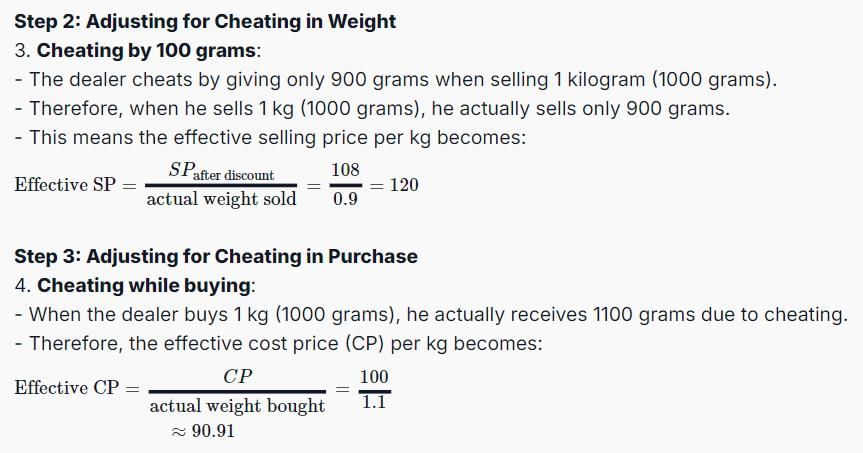
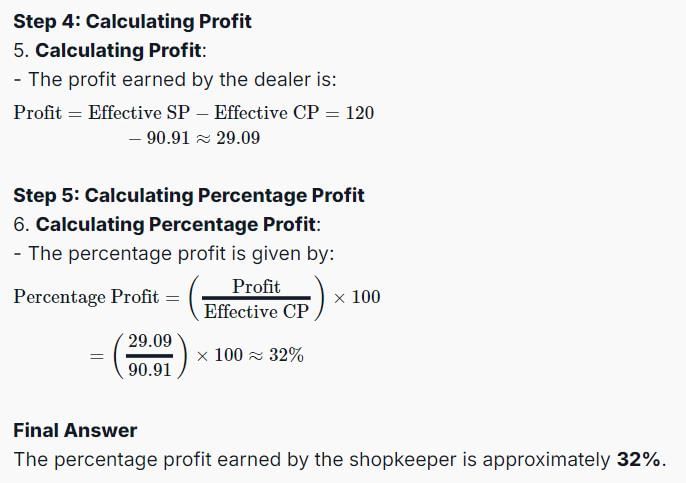
A dishonest dealer marks up the price of his goods by 20% and gives a discount of 10% to the customer. Besides, he also cheats both his supplier and his buyer by 100 grams while buying or selling 1 kilogram. Find the percentage profit earned by the shopkeeper.
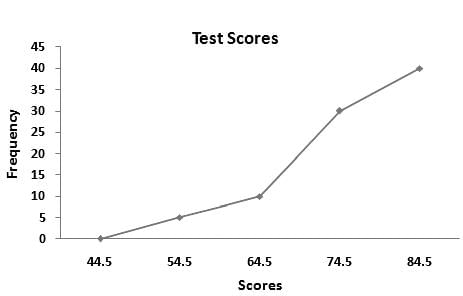
The graph represents the average score of a Test player with respect to the number of Test matches he played.
Determined the percentage change in average score b/w 10 - 40 match.
Out of the two bar graphs provided below, one shows the amounts (in Lakh Rs.) invested by a Company in purchasing raw materials over the years and the other shows the values (in Lakh Rs.) of finished goods sold by the Company over the years.
The value of sales of finished goods in 1999 was approximately what percent of the sum of amount invested in Raw materials in the years 1997, 1998 and 1999?
If A exceeds B by 40%, B is less than C by 20%, then find A ∶ C
The approximation of cos θ ≈ 1 is valid up to 3 decimal places as long as θ is less than:
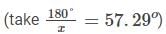
Which of the following functions cannot be the real part of a complex analytic function of z = x + iy?
Two objects of masses 2 kg and 3 kg are moving towards each other with velocities of 4 m/s and 2 m/s respectively. After the collision, the 2 kg object moves off with a velocity of 1 m/s in the opposite direction to its initial velocity. What is the velocity of the 3 kg object after the collision?
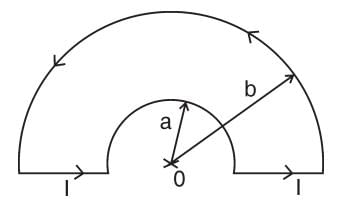
A loop made of copper wire is bent in the shape as shown in the figure below. The radius of the smaller semi-circular segment is ‘a’ and that of the larger semi-circular segment is ‘b’. If a current I flows in the loop, the magnetic field at the centre ‘0’ of the semi-circular segment is
The minimum energy of a collection of 6 non – interacting electrons of spin 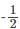 and mass m placed in a one-dimensional infinite square well potential of width L is
and mass m placed in a one-dimensional infinite square well potential of width L is
The potential of a diatomic molecule as a function of the distance between the atoms is given by V(r) = -a/ r6 + b/r12.The value of the potential at equilibrium separation between the atoms is:
With z=x+iy, which of the following function f(x,y) is not a (complex) analytic function of z?
If 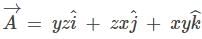 and C is the circle of the unit radius in the plane defined by z = 1, with the centre on the z-axis, then the value of integral
and C is the circle of the unit radius in the plane defined by z = 1, with the centre on the z-axis, then the value of integral 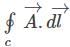 is:
is:
The first few terms in the Taylor series expansion of the function f(x) = sin x around x = π/4 are -
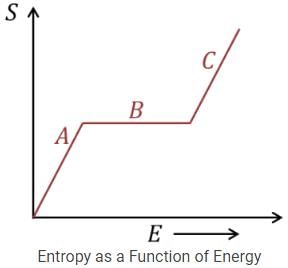
The entropy S of a thermodynamic system as a function of energy E is given by the following graph,
An electromagnetic wave is travelling in free space (of permittivity ε0) with electric field  The average power (per unit area) crossing planes parallel to 4x +3y = 0 will be:
The average power (per unit area) crossing planes parallel to 4x +3y = 0 will be:
Consider a 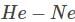 laser cavity consisting of two mirrors of reflectivity R1 = 1 and R2 = 0.98. The mirrors are separated by a distance d = 20 cm and the medium in between has a refractive index n0 = 1 and absorption coefficient a = 0. The values of the separation between the modes
laser cavity consisting of two mirrors of reflectivity R1 = 1 and R2 = 0.98. The mirrors are separated by a distance d = 20 cm and the medium in between has a refractive index n0 = 1 and absorption coefficient a = 0. The values of the separation between the modes  and the width
and the width 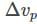 of each mode of the laser cavity are -
of each mode of the laser cavity are -
Assume that the noise spectral density at any given frequency, in a current amplifier is independent of frequency. The bandwidth of measurement is changed from 2 Hz to 30 Hz. The ratio (B/A) of the RMS noise current before (A) and after (B) the bandwidth modification?
The phonon dispersion for the following one-dimensional diatomic lattice with masses M1 and M2 (as shown in the figure)
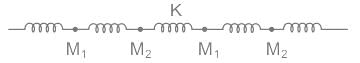
is given by
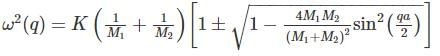
where a is the lattice parameter and K is the spring constant. The velocity of sound is
The vibrational motion of a diatomic molecule may be considered to be that of a simple harmonic oscillator with angular frequency ω. If a gas of these molecules is at a temperature T, what is the probability that a randomly picked molecule will be found in its lowest vibrational state?
If the reaction 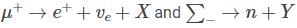 are governed by weak interactions, then the particle Z in the reaction, Y → Z + X is
are governed by weak interactions, then the particle Z in the reaction, Y → Z + X is
A particle of mass m is confined in an infinite square well with a shelf of height V0 extending half way across so that :
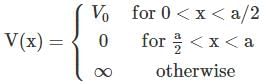
Using WKB approximation, the allowed energies En (n = 1, 2, 3,....) for this particle are, (given 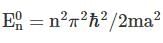 are the energies of particle in an infinite well with no shelf) :
are the energies of particle in an infinite well with no shelf) :
The spectral line corresponding to an atomic transition from J=1 to J=0 states splits in a magnetic field of 1KG into three components separated by 1.6×10−3. If the zero field spectral line corresponding to 1849, what is the g− factor corresponding to the J=1 state? ( You may use 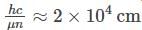 )
)




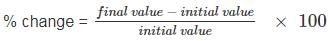
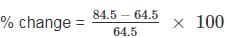
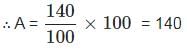
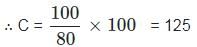

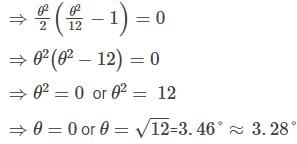
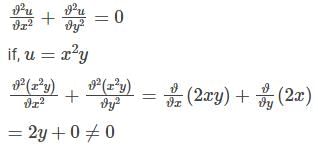
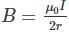
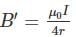

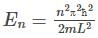
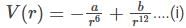
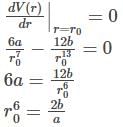
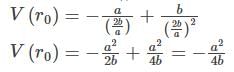
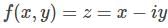 Cauchy Riemann condition is not satisfied, therefore function is not analytic function of z.
Cauchy Riemann condition is not satisfied, therefore function is not analytic function of z.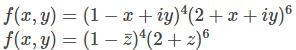
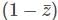 is not analytic function and (2+z) is analytic function. Therefore product of these two functions is not be analytic.
is not analytic function and (2+z) is analytic function. Therefore product of these two functions is not be analytic.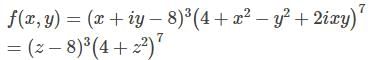
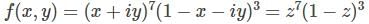
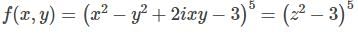
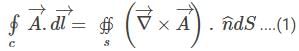
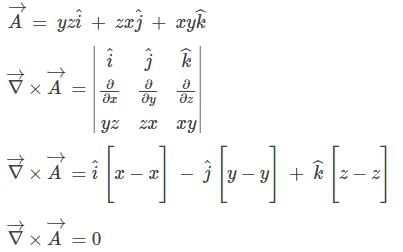
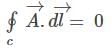
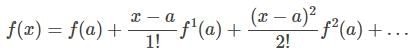
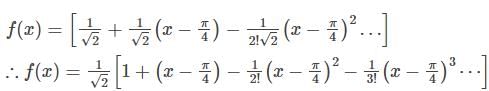
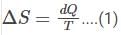
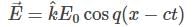
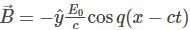
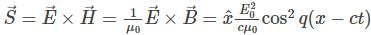
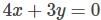 is
is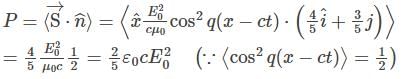
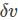 is given as,
is given as,
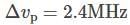
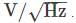
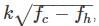
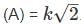
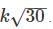
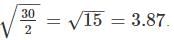
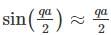
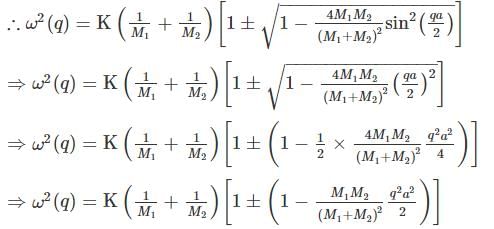
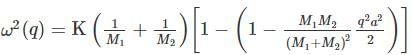
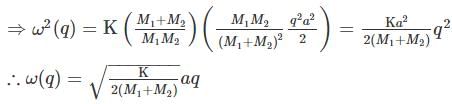
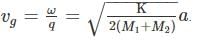
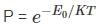
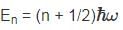
 is the Planck constant.
is the Planck constant.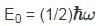
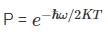
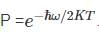
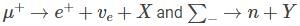 using conservation laws
using conservation laws 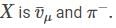
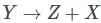 we have
we have 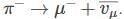 Thus,
Thus, 
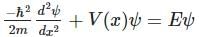
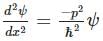 where
where 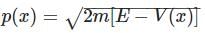
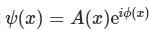 is the value for any wavefunction.
is the value for any wavefunction.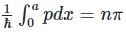
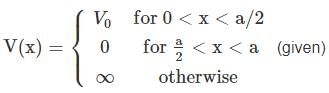
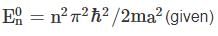
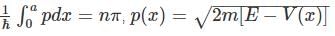
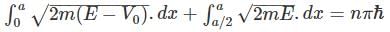
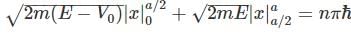
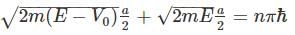
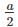 and
and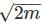 to right hand side, we get,
to right hand side, we get, 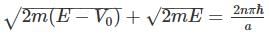
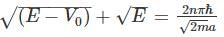
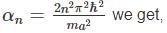
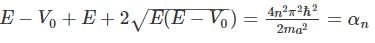
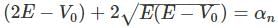
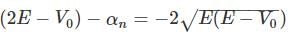
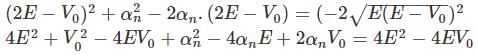
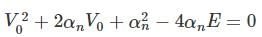
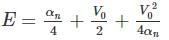
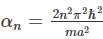 in above equation, we get,
in above equation, we get,