Practice Test: Polity- 1 - UPSC MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Practice Test: Polity- 1
Consider the following statement regarding changes made by the Indian Independence Act of 1947 in the position of Constituent Assembly.
a. The Constituent Assembly was made a fully sovereign body.
b. The Constituent Assembly became the first Parliament of free India.
c. When the Constituent Assembly met as the Legislative body it was chaired by Dr. Rajendr Prasad.
d. The total strength of the Constituent Assembly came down to 299 as against 389.
a. The Constituent Assembly was made a fully sovereign body.
b. The Constituent Assembly became the first Parliament of free India.
c. When the Constituent Assembly met as the Legislative body it was chaired by Dr. Rajendr Prasad.
d. The total strength of the Constituent Assembly came down to 299 as against 389.
The language and ideals of the Preamble of Constitution of India is influenced / borrowed from which of the following constitution(s)?
1. USA
2. France
3. Australia
Select the correct option from the codes given below:
1. USA
2. France
3. Australia
Select the correct option from the codes given below:
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The writ of prohibition is not available against:
1. Quasi-judicial authority
2. Administrative authority
3. Legislative body
Choose from the following options.
1. Quasi-judicial authority
2. Administrative authority
3. Legislative body
Choose from the following options.
The writ of mandamus cannot be issued:
1. Against a private individual or body
2. To enforce departmental instruction that does not possess statutory force
3. When the duty is mandatory
Choose from the following options.
Consider the following statements.
Assertion (A): The constitution authorises the President to suspend the right to move any court to enforce certain Fundamental Rights during a National Emergency.
Reason (R): All fundamental rights are automatically suspended with a proclamation of National Emergency.
In the context of the above, which of these is correct?
Consider the following statements about the office of the President of India.
1. No person has occupied the office for more than one complete term.
2. Every President has served the full term of office.
Q. Which of the above is/are correct?
Consider the following statements about Cabinet Committees:
1. They are not mentioned in the Constitution.
2. They are set up by the Prime Minister according to the exigencies of the time and requirements of the situation.
3. The Cabinet cannot review the decisions taken by Cabinet Committees.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Consider the following concerning the relationship between the President, Prime Minister and the Council of Ministers.
1. In normal circumstances, the council of Ministers' advice is constitutionally binding on the President.
2. The nature of advice tendered by ministers to the President can be enquired by a higher court to ascertain malpractices in administration.
3. The council of ministers ceases to hold office immediately after the dissolution of the Lok Sabha by the President.
Select the correct answer using the codes below.
Consider the following statements:
1. Article 137 of the Constitution gives the Supreme Court the power to review any of its judgments or orders
2. It is not necessary that only parties to a case can seek a review of the judgment on it. Any person aggrieved by a ruling can seek a review
Which of these statements are correct?
Consider the following statements.
1. Judiciary is the final interpreter of the Constitution
2. Judiciary has the final power to strike down laws passed by the Parliament if they violate the Constitution's basic structure of the constitution.
Which of the above is/are correct?
Consider the following statements with respect to Freedom of Religion enshrined in the Constitution:
1. It includes the freedom to not follow any religion.
2. It bars all religious conversions.
3. It is not applicable to foreign nationals.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Consider the following statements.
1. The Oath of office to the Governor is administered by the Chief Justice of the Supreme Court
2. In the absence of chief justice of the Supreme Court, The Oath is administered by the senior-most judge of the Court
Which of these statements is/are correct?
Consider the following statements.
1. The Chief Minister cannot be dismissed by the Governor as long as he enjoys the majority support in the legislative assembly.
2. The salary and allowances of the chief minister are determined by the state legislature.
Which of these statements is/are correct?
Which of the following are correctly matched?
1. Conduct of business of the Government of a State - Article 166
2. Council of Ministers to aid and advise governor - Article 164
3. Duties of Chief Minister - Article 167
Choose from the following options.
Consider the following statements about the Legislative Council.
1. The vacant seats are filled up by fresh elections and nominations at the beginning of every third year
2. The retiring members are not eligible for re-election and re-nomination any number of times
Which of these statements are correct?
Consider the following statements of the power of the Superintendence of the High Court.
1. The High Court has this power over all courts and tribunals including those dealing with the armed forces functioning in the state
2. In the exercise of this power it may May issue general rules and prescribe forms for regulating the practice and proceedings of such courts
Which of these statements is/are correct?
Consider the following statements.
1. At the lowest level, on the civil side, is the Court of Munsiff and on the criminal side, is the Court of Judicial Magistrate
2. The munsiff possesses limited jurisdiction and decides civil cases of small pecuniary stake
Which of these statements are correct?
Which of the following sentence/sentences is/are correct?
1. The High Court of Jammu and Kashmir will be the common High Court for the Union Territories of Ladakh, and Jammu and Kashmir
2. The Union Territory of Jammu and Kashmir will have an Advocate General to provide legal advice to the government of the Union Territory
Choose from the following options.
With reference to the seventh schedule of the Indian constitution, consider the following pairs:
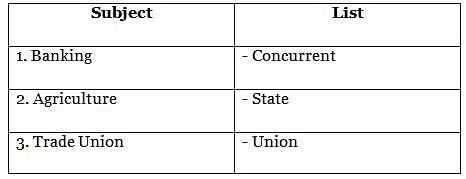
How many pairs given above are correctly matched?
Which of the following statements is/are correct with regard to the consequences of the proclamation of a Financial Emergency?
1. Centre acquires full control over the states in financial matters.
2. President may reserve all money bills or other financial bills for consideration after they are passed by the legislature of
the state.
3. President may issue directions for the reduction of salaries and allowances of the judges of the Supreme Court and the
high court.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
Which of the following rights are assured under the Right to Life and Liberty of the Indian Constitution?
1. Right to die through Passive Euthanasia
2. Right to appropriate Life Insurance Policy
3. Right not to be subjected to Narco Analysis test
4. Right to travel abroad
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
Consider the following statements regarding the amendment procedure of the constitution of India:
1. A constitutional amendment bill cannot be introduced by the nominated members of the Lok sabha.
2. A constitutional amendment bill that seeks to amend the federal provisions of the Constitution must be ratified by the
Legislatures of half of the States by a special majority.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
India was a pioneer when it comes to giving voting rights to the people. In this context, which of the following countries gave universal adult franchises after India?
1. United States of America
2. Japan
3. France
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
Consider the following provisions of the Indian Constitution:
1. Fundamental Rights
2. Directive Principles of State Policy
3. Fundamental Duties
Which one of the following amendments have made changes in all of the given above parts?
Which of the following statements is/arecorrect regarding Fundamental Rights?
1. They are sacrosanct in nature and cannot be amended.
2. They are available against the actions of both State and private individuals.
3. They operate as checks on the tyranny of both executive and the Legislature.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
Which of the following is/are features of Indian secularism as adopted in the Constitution?
1. Religion is a personal matter and there is no interference by the state.
2. No citizen can be denied entry into any educational institute of the state on the grounds of religion or caste.
3. Every religious denomination has the right to establish and maintain charitable institutions without any limitation.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
Which of the following bodies/institutionsis/are audited totally and directly by the CAG?
1. Reserve Bank of India
2. Oil and Natural Gas Commission
3. Life Insurance Corporation of India
4. State Bank of India
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
Which of the following provisions in the constitution can be amended by a simple majority?
1. Establishment of the new states
2. Termination of citizenship
3. Election of the President
Select the correct code using the code given below:
Which of the following renewable-rich states are included under Green Energy Corridor Project?
1. Tamil Nadu
2. Rajasthan
3. Punjab
4. Jharkhand
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
The Directive Principles of State Policy are enumerated in Part IV of the Constitution from Articles 36 to 51. In this regard, the framers of the Constitution derived inspiration from which of the following?
- The Irish Constitution
- Instrument of Instructions enumerated in the Government of India Act of 1935.
- Gandhian ideology
- Freedom struggle of India
Select the correct answer using the code given below.

















