Practice Test: Environment- 1 - UPSC MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Practice Test: Environment- 1
Which of the following are natural World Heritage Sites in India as mandated by UNESCO?
1. Kaziranga National Park
2. Keoladeo National Park
3. Sundarbans National Park
4. Valley of Flowers National Park
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
The concept of "Edge effect" in ecology is best defined as which of the following?
Consider the following pairs:
Elephant Reserves - State
1. Lemru - Chhattisgarh
2. Chirang-Ripu - Meghalaya
3. Singphan - Jharkhand
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
Elephant Reserves - State
1. Lemru - Chhattisgarh
2. Chirang-Ripu - Meghalaya
3. Singphan - Jharkhand
Consider the following features:
1. Sharing similar resources
2. Competing for similar resources
3. Interbreeding and reproduction
How many of the above are distinguishing features of a population in ecology?
The 2023 Production Gap Report titled “Phasing down or phasing up? Top fossil fuel producers plan even more extraction despite climate promises” was recently released. In this context, consider the following statements:
1. The report is published by the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC).
2. The report tracks the discrepancy between governments’ planned fossil fuel production and global production levels consistent with limiting warming to 1.5°C or 2°C.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
With reference to the National Parks in India, consider the following statements:
1. The central government can declare a national park.
2. The State government has all the rights of lands to be included in the national parks.
3. Only on the recommendation of the National Board for Wildlife (NBWL), the boundaries of national parks can be changed.
How many of the above statements are correct?
With reference to the Kaziranga National Park, consider the following tags:
1. Tiger Reserve
2. Important Bind Area recognized by BirdLife International
3. World Heritage Site of UNESCO
How many of the above tags are associated with Kaziranga National Park?
With reference to the Conservation reserve, consider the following statements:
1. It is notified by State Government after consulting with the Central government and the local communities.
2. They act as buffer zone and migration corridors between national parks, wildlife sanctuaries and reserved and protected forests.
3. India’s first conservation reserve for Dugongs has been set up in Palk Bay.
How many of the above statements are correct?
Which of the following correctly describes the theme of UN decade of 2021-30?
If any wild animal specified in Schedule I of the Wild Life (Protection) Act, 1972 has become dangerous to human life, who among the following permits any person to hunt such animal?
How many of the following types of adaptations are shown by mangroves?
1. Viviparity
2. Cutinized epidermis
3. Pneumatophores
4. Knee roots
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
Consider the following statements regarding Leith’s Softshell Turtle:
1. It is a large freshwater turtle which is endemic to peninsular India.
2. It has the least concern status by IUCN.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Consider the following statements:
1. A protected forest can be a reserved foresstt bbuu t a reserved forest cannot be a proteecctteedd forest.
2. Rules for regulating the management of the village forest is made by the State Government.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
In the context of ecological niches, the term "Fundamental niche" refers to,
Arrange the following organisms in the correct sequential order of a food chain, starting from the primary producer to the top predator.
1. Desert Hare
2. Desert willow
3. Coyote
4. Falcon
5. Snake
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
With reference to The Man and the Biosphere (MAB) programme, consider the following statements:
1. It is an intergovernmental programme launched in 1971 by UNESCO for improving people's relationships with environment.
2. Biosphere Reserves des ignat ion criteria includes large protected core area enough to sustain viable populations representing all trophic levels.
3. It is governed by International Coordinating Council (ICC), reporting to UNESCO.
How many of the above statements are correct?
Consider the following statements regarding the Marine Protected Areas (MPAs):
1. They are notified as ‘national parks’ or ‘wildlife sanctuaries’ under Wildlife Protection Act, 1972.
2. Coastal and marine sites are identified and prioritized as Important Coastal and Marine Areas by the Wildlife Institute of India.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
The Horn of Africa experiences increased rainfall during which of the following weather phenomena?
1. El Nino
2. La Nina
3. Positive Indian Ocean Dipole
4. Negative Indian Ocean Dipole
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
Consider the following statements with respect to the e-way bill system under the Goods and Services Tax (GST):
1. A consignment value of more than ?50,000 is required to generate an e-way bill for movement between the two States and within a State.
2. With regard to intrastate movement of goods, each state is free to choose a threshold value for e-way bill generation.
3. No e-way bill is required for goods transported by a non-motorized conveyance.
How many of the above statements are correct?
Consider the following statements regarding the World Network of Biosphere Reserves (WNBR):
1. It was formed in 1971 for biodiversity conservation, ecosystem restoration, and living in harmony with nature.
2. More than 50 percent of the notified biosphere reserves in India are a part of the WNBR.
3. Sundarbans Biosphere Reserve was the first to be recognized under the WNBR.
How many of the above statements are correct?
With reference to the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework, consider the following statements:
1. It was adopted during the sixteenth meeting of the Conference of the Parties (COP 16) to the Convention on Biological Diversity.
2. It aspires to restore 30% of degraded lands and marine areas by 2030.
3. It targets to reduce the rate of introduced invasive species by 50 percent by 2030.
How many of the a correct?
With reference to the Indian Elephants, consider the following statements:
1. It is the National Heritage animal and is depicted on the frieze of the circular abacus of the State Emblem.
2. Elephant census is conducted once in 5 years.
3. There are around 50 Elephant Reserves in India.
How many of the above statements are correct?
Consider the following statements with respect to Greenhouse Gas Bulletin:
1. It is an initiative of the United Nations Environment Programme.
2. The bulletin shows the globally averaged surface mole fractions for carbon . dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O) and compares them with the previous year and preindustrial levels.
3. It is published semi-annually.
How many of the above statements are correct?
Consider the following approaches for the conservation of biodiversity:
1. Germplasm banks
2. Tissue culture
3. Cryopreservation
4. DNA clones
How many of the above techniques are in- vitro techniques for the conservation of biodiversity?
With reference to the Environment and Ecology, consider the following statements:
Statement-I: Ecology is basically concerned with four levels of biological organisation like organisms, populations, communities and biomes.
Statement-II: Ecology examines individual organisms and their adaptations to their environment.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
Consider the following statements:
1. Populations refer to groups of individuals of the same species living in a particular area.
2. Communities consist of single population of particular species living and interacting in the same area.
3. Biomes are large-scale ecological regions characterized by distinct climate, vegetation, and animal communities.
How many of the above statements are correct?
With reference to the species, consider the following statements:
Statement-I: The size of a population for any species is not a static parameter.
Statement-II: It keeps changing with time, depending on various factors including food availability, predation pressure and adverse weather.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
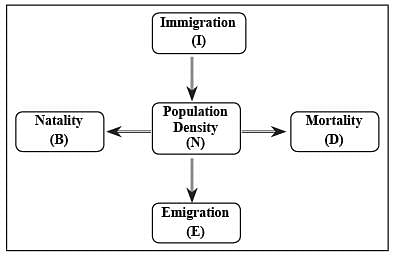
The population size of any species depends upon which of the following factors?
1. Natality and immigration contribute to a decrease in population density.
2. Mortality and emigration contribute to an increase in population density.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
Match the following pairs:
1. Natality - It refers to the number of births during a given period in the population that are added to the initial density.
2. Mortality - It is the number of deaths in the population during a given period.
3. Immigration - It is the number of individuals of the same species that have come into the habitat from elsewhere during the time period under consideration.
4. Emigration - It is the number of individuals of the population who left the habitat and gone elsewhere during the time period under consideration.
How many of the above pairs is/are correctly matched?