Practice Test: Geography- 2 - UPSC MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Practice Test: Geography- 2
Which of the following best describes the term "truck farming"?
The nomadic tribes named the Lapps, the Yakuts, and the Samoyeds belong to which of the following regions?
Consider the following :
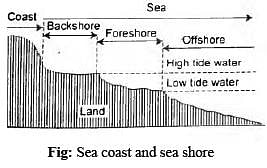
- The back shore represents the beach zone, starting from the limit of frequent storm waves to the cliff base.
- Foreshore extends from low tide water to high tide water.
- Offshore represents the zone of shallow bottom of the continental slope.
How many of the above given statements are correct regarding the sea coast and the seashore?
With reference to the ‘erosional processes’, consider the following statements:
- Hydraulic action is the mechanical loosening and removal of materials of rocks by water alone without the help of erosion tools.
- Attrition is the process of removing, lifting and blowing away dry and loose particles of sand and dust by winds.
- Deflation refers to the wearing down and rounding of sediment particles as they collide with each other during transport.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
Consider the Following:
- Gorges
- Plunge Pools
- Rapids
- Crevasses
How many of the above are erosional landforms formed by the running water?
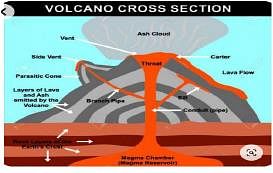
Consider the following statements about Volcanoes:
- Magma once it starts moving towards the crust or it reaches the surface, is referred to as lava.
- The Hawaiian volcanoes are famous examples of shield volcanoes.
Which of the statements given above are incorrect?
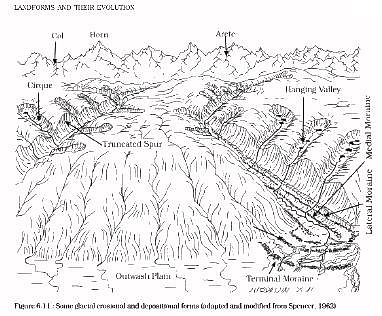
Which of the following are examples of Erosional landforms of Glaciation?
- Eskers
- Aretes
- Bergschrund
- Moraines
- Drumlins
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Consider the following statements:
- Straight Channels are found where there is the same structure and parallel disposition of hard and soft rocks on the underlying topography.
- A Meandering Channel shows both the erosion as well as deposition features.
- A Braided Channel is formed when a stream contains too much sediment, and the stream divides into branching and intertwining subchannels.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
“The heavy rainfall, the warm summers and the damp air from fogs, all favour the growth of trees. Forests are adaptable to cold conditions. The trees occur in almost pure stands and timber is a leading export item of this region. A long growing season of over six months and an adequate supply of moisture from maritime sources encourage rapid growth of ferns.”
Which of the following climatic types is best described by the passage above?
Consider the following pairs:
Geographical feature : Associated River
- Gandikota Canyon : Kaveri
- Gangani : Shilabati
- Raneh Fall : Betwa
- Vazhachal Falls : Bharathappuzha
How many of the above pairs are incorrectly matched?
“Winters are long and very severe; summers are cool and brief. In some areas of this climate, there are weeks of continuous darkness.”
Which one of the following climatic regions is best described by the above paragraph?
Which of the following statements about types of lava are correct?
- Basic lavas are rich in Iron and Magnesium but poor in Silica.
- Basic lavas flow quietly and are not very explosive.
- Acidic lava is highly fluid and affects extensive areas.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Consider the following statements:
Statement-I: There are no big trees in the tundra region.
Statement-II:The tundra region is deficient in heat.
Which of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
Consider the following pairs:
River course : Landforms
- Upper : V shaped Valleys
- Middle : Estuaries
- Lower : Ox-bow lakes
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
Consider the following:
- Lapilli
- Volcanic dust
- Volcanic bombs
- Volcanic ash
Which of the following is the correct ascending order of the size of the given pyroclastic materials?
With reference to nutrient content, which one of the following correctly describes the alluvial soils?
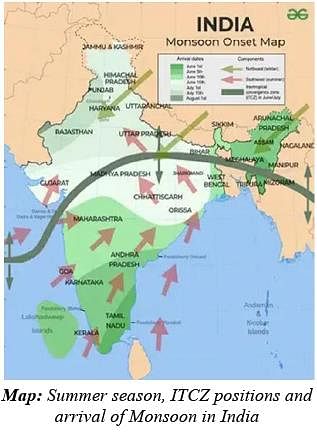
Consider the following statements regarding the summer weather patterns in the Indian subcontinent:
- The Inter Tropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) shifts southward during the summer season.
- Westerly jet stream over the North Indian Plain strengthens as the summer progresses.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
With reference to the 5th National Family Health Survey (NFHS-5) consider the following statements:
- The overall sex ratio in India is better than the sex ratio at birth.
- The overall sex ratio in India is higher in urban areas than in rural areas.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
Which of the following states do not have any notified Scheduled Tribes as per the 2011 Census?
- Gujarat
- Goa
- Punjab
- Haryana
- Bihar
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Which one of the following states has the highest percentage of rural population as per the 2011 Census?
Which one of the following religious groups have the highest proportion of literate population in India?
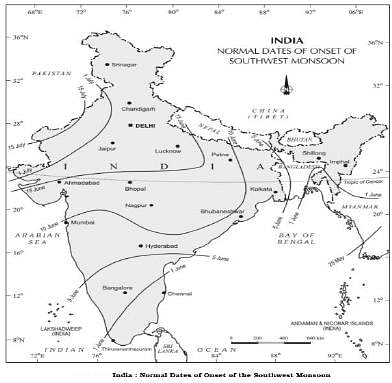
Consider the following statements regarding the Indian monsoon and its onset:
- The differential heating of land and sea during summer is responsible for the onset of the Indian monsoon.
- The southwest monsoon is a continuation of the southeast trades after crossing the Equator.
- The westerly jet stream of Nothern India bring the burst of the monsoon with it.
- By mid-July, southwest monsoon spreads to the entire subcontinent.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
Consider the following statement with reference to the Universal Postal Union:
- It is a specialized agency of United Nation which promotes cooperation between postal sector players.
- Only members of United Nations can be the member of the Union.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
Which one of the following is correct with reference to the term ‘Population Momentum’?
Consider the following statements with reference to the Producer Organisations (PO):
- A producer Organisation is formed by farmers only.
- It is an organization of the producers, by the producers and for the producers.
- The maximum number of members in the organization is restricted to ten members only.
How many of the statements given above are incorrect?
Consider the following:
- Khasi and Jaintia hills
- Ladakh
- Deccan Plateau
- Northern plains
Which of the following is the correct order of decreasing rainfall for the above regions?
With reference to Carbon Capture and Storage technology, which of the following statements is correct?
- The Possible storage sites for carbon emissions include saline aquifers or depleted oil and gas reservoirs.
- United States was the first country to utilize this technology.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Consider the following statements:
- Replacement level is the rate of growth required for new generations to replace the older ones that are dying out.
- Total Fertility Rate (TFR) of 2 is known as the replacement rate.
- India’s TFR is more than the Replacement level fertility rate.
How many of the above statements are correct?
Consider the following statements with reference to the Farmers Distress Index:
- It is published by Central Island Agricultural Research Institute.
- Its main goal is to minimise the agrarian distress in the form of crop loss and income shock.
- The degree of distress will be identified on the basis of twenty one questions.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
Consider the following statements:
- The natural growth of the population is assessed through crude birth and death rates.
- The induced growth of the population is explained by migration patterns of the population.
Which of the statements given above are correct?