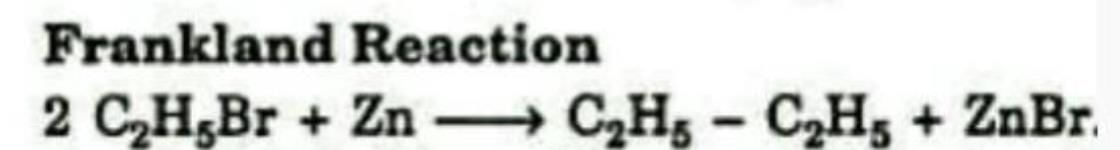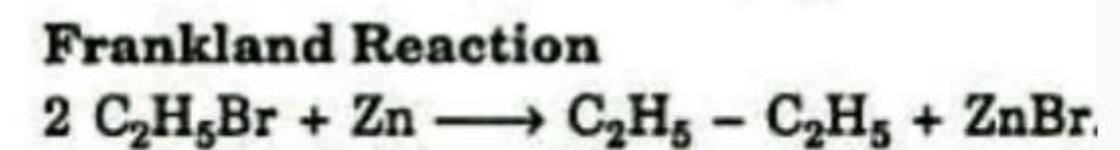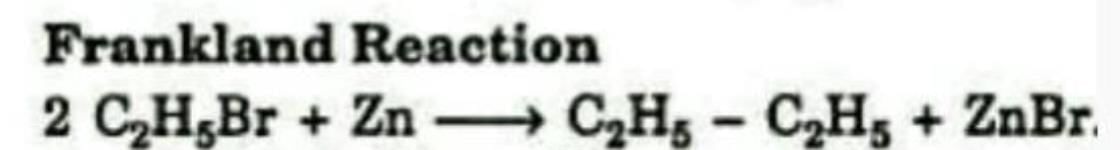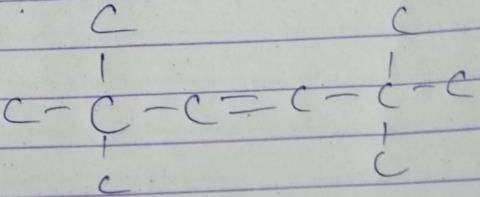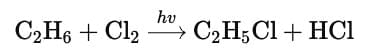Test: Alkanes & Cycloalkanes - NEET MCQ
24 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Alkanes & Cycloalkanes
Direction (Q. Nos. 16 - 18) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc.
Three questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (cj and (d).
Passage
A hydrocarbon with molecular formula C10H18, upon catalytic hydrogenation gives C10H20 (X). X on free radical chlorination gives two monochloro derivatives with their molecular formula C10H19CI that are constitutional isomers.
Q. Which of the following satisfy the criteria of X ?
Three questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (cj and (d).
Which of the following statem ents regarding free radical halogenation of alkane is not true?
Formation of an alkane from the reduction of an alkyl halide with Zn is known as
Formation of an alkane from the reduction of an alkyl halide with Zn is known as
Consider the following bromination reaction.
If a pure enantiomer of reactant is taken in the above reaction, the correct statement concerning product dibromide is/are
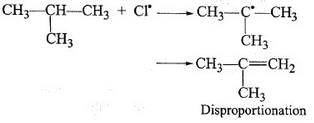
During free radical bromination of isobutane, an alkene is produced as by product via disproportionation of the intermediate alkyl free radical. What is this alkene?
A hydrocarbon with molecular formula C10H18, upon catalytic hydrogenation gives C10H20 (X). X on free radical chlorination gives two monochloro derivatives with their molecular formula C10H19CI that are constitutional isomers.
Q. Which of the following reactions can synthesise X ?
Theoretically, how many different monocarboxylic acids on heating with soda lime gives, 3-methyl pentane?
Direction (Q. Nos. 12 -15) This section contains 4 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
Q. In the following free radical bromination reaction, the important product(s) is/are
Which of the following reactions can bring about chlorination of cyclohexane?
Find the correct order for relative energies of the ethane conformations
The major monobromination product which results when ethyl cyclohexane is subjected to free radical bromination, is
Formation of an alkane from the reduction of an alkyl halide with Zn is known as
From following list, how many of them upon catalytic hydrogenation would produce more heat than that produced in catalytic hydrogenation of frans-2-butene?

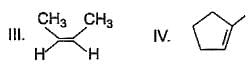
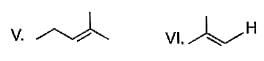

Which of the following is not a possible termination step in the free radical chlorination of methane?
Direction (Q. Nos, 19 - 22) This section contains 4 questions. When worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).
Q. How many different isomers of alkenes {including stereoisomers) exist that all upon catalytic hydrogenation adds one mole of H2 to give the same 2, 2, 3,5-tetramethyl hexane?
What is relative reactivity of secondary versus primary hydrogens in free radical bromination of n-butane if the ratio of 1-bromo to 2-bromobutane formed is 7 : 39?
What is the bromination product in the following reaction?
What is/are true regarding free radical iodination of an alkane?
Arrange the following in increasing order of boiling points.
I. 3 -methyl pentane
II. 3-chloropentane
III. 3-bromopentane
IV. 3,3-dichloropentane
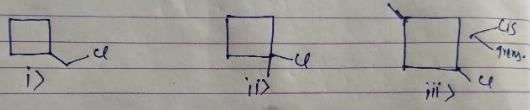
How many different monochlorination products would be obtained on free radical chlorination of methyl cyclobutane?
A hydrocarbon with molecular formula C10H18, upon catalytic hydrogenation gives C10H20 (X). X on free radical chlorination gives two monochloro derivatives with their molecular formula C10H19CI that are constitutional isomers.
Q. How many different alkenes on hydrogenation, can gives X ?
Direction (Q. Nos. 1 - 11) This section contains 11 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. When light is shined on a mixture of chlorine and ethane, chloroethane is formed besides dichloroethane, trichloroethane and several other products. What reaction condition can optimise the yield of chloroethane?