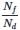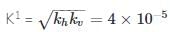Test: Soil Mechanics & FM- 1 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Soil Mechanics & FM- 1
As per ISS the specific gravity of soil is determined at
The degree of saturation in soils can be defined as the ratio of –
When the pores of a soil are full of water then the soil sill be called –
A dry soil has a mass specific gravity of 1.35. It the specific gravity of solids is 2.7. then the voids ratio will be –
The natural water content of the soil sample was found to be 40%, specific gravity is 2.7 and void ratio 1.2 then the degree of saturation of the soil will be –
A functional equation of specific gravity (G) water content (w), void ratio (e) and degree of
saturation (sr) is :-
The soil having unitormity coefficient less than 4 is called
The uniformity co-efficient of soil is defined as the ratio of -
A flow net for seepage under a sheet pile wall has nf = 4 nd = 8 and the permeabilities of the soil in the horizontal direction are kh = 8× 10–5 m/sec and kv = = 2 × 10-5 m/sec. If the head loss through the soil is 2m, the quantity of seepage per meter length of the wall will be -
The percentage of porosity of loose sand is in the range -
The shear strength of a soil in the liquid limit state is –
When the plastic limit of a soil is greater than the liquid limit, then the plasticity index is –
The law that states that laminar flow in a saturated soil, the velocity is directly proportional to hydraulic gradient is called –
The e-log p curve shown in the figure is representative of –
Which of the following is not an assumption in the terzaghic's theory of one diamensional consolidation
A clay sample has a void ratio of 0.50 in dry state and specific gravity of solids = 2.70 its shrinkage limit will be –