BPSC Prelims Past Year Paper- 2022 - BPSC (Bihar) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - BPSC Prelims Past Year Paper- 2022
Who established trade relations with Roman empire?
The Muslim ruler whose empire was regarded as a part of Dar-ul-Islam was
Who among the following opposed the power of the Khalifa?
Tughril Khan raised a standard of revolt during whose reign?
Who was the first Mughal ruler who fought against the British?
Which of the following were the social reforms introduced by William Bentinck?
1. Abolition of Sati
2. Abolition of slavery
3. Removal of disabilities due to change of religion
4. Suppression of the organized bands of Thugs.
Choose the correct answer from the codes given below.
In which year, first Census was introduced in India?
On which date, Sukhdev, Bhagat Singh and Rajguru were hanged?
Who was the third Satyagrahi of Individual Satyagraha launched by Mahatma Gandhi in 1940?
Who launched secret radio during the Quit India Movement?
Who was the Physician of Magadh ruler Bimbisara?
Who was the real founder of Turk rule in Bihar?
In which year the Chuar Revolt of Bihar took place?
In which year was Orissa separated from Bihar?
Where was the first Buddhist Council convened?
Which Gupta ruler assumed the throne after killing his elder brother?
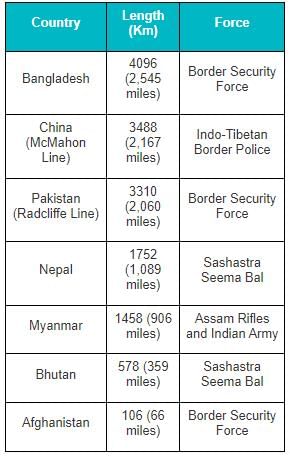
What is the boundary line between India and China called?
Consider the following statements :
1. In India, the Project Tiger was launched in 1973.
2. The theme for International Biodiversity in 2022 is ‘Building a shared future for all life'.
3. The Project Tiger is a tiger conservation programme.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Which State in India is the leading producer of thorium?
At which of the following places the newsprint paper industry is located?
According to the Census of India, 2011 which Scheduled Tribe is largest in India?