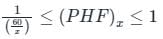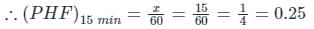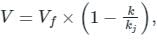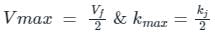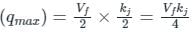Test: Highway Transportation- 1 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Highway Transportation- 1
In 1927, Jayakar committee was set up to examine and report on road development in India,abased on which certain institutions were subsequently set certain institutions were subsequently set up. Which of the following were the direct out come of Jayakar committee recommendations.
1. Indian Road Congress
2. Central Road fund
3. CRRI
4. National Highway Act
The semiofficial body set up for controlling and standardization of roads and bridges in India is
Which of the following roads are congested during peak hours?
The road connecting a district headquarters of one state to the district headquarters of neighbouring state is called
Major district roads connect market and production areas within a district to
The city roads providing an access to residence, business and other buildings are called
The branch of engineering that deals with improvement of traffic performance, traffic studies and traffic network is called
Which of the following statement is correct? According to the principle of road alignment
In the final survey the centre line stakes are driven at interval in plain terrain.
In the final survey the centre line stakes are driven at interval in hilly terrain.
In preliminary survey of a road project, in hilly region cross sections are taken generally at.
Consider the following statements in the context of the geometric design of roads
I: A simple parabolic curve is an acceptable shape of summit curves
II: Comfort to passengers is an important consideration in the design of summit curves.
The correct option evaluating the above statements and their relationship is
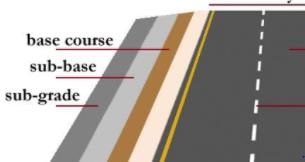
The portion of the roadway between outer edges of carriageway and drains in case of cuttings is known as
The minimum value of 15 minute peak hour factor on a section of a road is
The traffic starts discharging from an approach an intersection with the signal turning green. The constant headway considered from the fourth or fifth headway position is referred as
The speed-density relationship in a mid-block section of a highway follows the Greenshields’s model. If the free flow speed is vf and the jam density is kj , the maximum flow observed on this section is
Two cars P and Q are moving in a racing track continuously for two hours. Assume that no other vehicles are using the track during this time. The expressions relating the distance travelled d (in km) and time t (in hour) for both the vehicles are given as
P (d) = 60t
Q (d) = 60t2
Within the first one hour, the maximum space headway would be