AC can be stepped up/down efficiently using transformers, which is the key advantage over DC. (b) is actually a DC advantage for very long distances; (c) and (d) aren’t generally true.
Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam > Electrical Engineering (EE) Tests > Test: Power Systems - 1 - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
Test: Power Systems - 1 - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
Test Description
25 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Power Systems - 1
Test: Power Systems - 1 for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Test: Power Systems - 1 questions and answers have been prepared
according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus.The Test: Power Systems - 1 MCQs are made for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 Exam.
Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Test: Power Systems - 1 below.
Solutions of Test: Power Systems - 1 questions in English are available as part of our course for Electrical Engineering (EE) & Test: Power Systems - 1 solutions in
Hindi for Electrical Engineering (EE) course.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Test: Power Systems - 1 | 25 questions in 50 minutes | Mock test for Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study for Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Detailed Solution for Test: Power Systems - 1 - Question 1
Detailed Solution for Test: Power Systems - 1 - Question 2
Test: Power Systems - 1 - Question 3
The main advantage of AC transmission system over DC transmission system is
Detailed Solution for Test: Power Systems - 1 - Question 3
Test: Power Systems - 1 - Question 4
In any case, where the height of transmission tower is increased
Detailed Solution for Test: Power Systems - 1 - Question 4
Test: Power Systems - 1 - Question 5
Series capacitors on transmission lines are of little used when
Detailed Solution for Test: Power Systems - 1 - Question 5
Test: Power Systems - 1 - Question 6
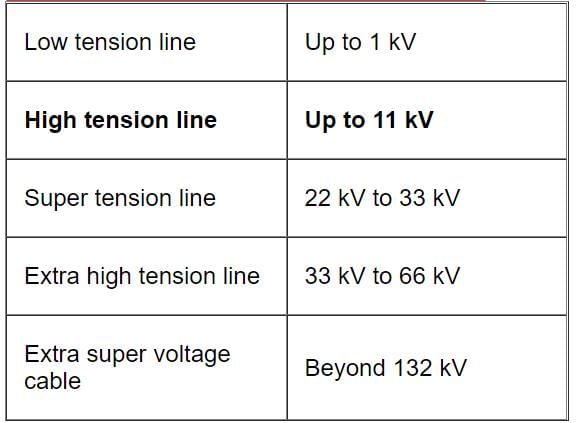
Which of the following is not a standard transmission voltage?
Detailed Solution for Test: Power Systems - 1 - Question 6
Detailed Solution for Test: Power Systems - 1 - Question 7
Detailed Solution for Test: Power Systems - 1 - Question 8
Detailed Solution for Test: Power Systems - 1 - Question 9
Detailed Solution for Test: Power Systems - 1 - Question 10
Detailed Solution for Test: Power Systems - 1 - Question 11
Detailed Solution for Test: Power Systems - 1 - Question 12
Detailed Solution for Test: Power Systems - 1 - Question 13
Detailed Solution for Test: Power Systems - 1 - Question 14
Detailed Solution for Test: Power Systems - 1 - Question 15
Detailed Solution for Test: Power Systems - 1 - Question 16
Test: Power Systems - 1 - Question 17
What is the type of insulator used for holding the HT overhead conductor on the straight running of poles?
Detailed Solution for Test: Power Systems - 1 - Question 17
Test: Power Systems - 1 - Question 18
What is the types of insulators used at dead ends and on straight lines as suspension type for voltage 3.3 kV and above ?
Detailed Solution for Test: Power Systems - 1 - Question 18
Detailed Solution for Test: Power Systems - 1 - Question 19
Detailed Solution for Test: Power Systems - 1 - Question 20
Detailed Solution for Test: Power Systems - 1 - Question 21
Detailed Solution for Test: Power Systems - 1 - Question 22
Detailed Solution for Test: Power Systems - 1 - Question 23
Detailed Solution for Test: Power Systems - 1 - Question 24
Test: Power Systems - 1 - Question 25
Two pin sockets should not be used in domestic wiring unless the appliance to be connected is
Detailed Solution for Test: Power Systems - 1 - Question 25
Information about Test: Power Systems - 1 Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Test: Power Systems - 1 solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Test: Power Systems - 1, EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice
Download as PDF