Test: Atoms and Nuclei - 2 - CUET MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Atoms and Nuclei - 2
The ionisation potential of hydrogen is 13.6 V. The energy required to remove an electron from the second orbit of hydrogen is
The radius of first Bohr orbit is r. What is the radius of 2nd Bohr orbit?
We wish to see inside an atom. Assuming the atom to have a diameter of 100 pm, this means that one must be able to resolve a width of say 10 pm. If an electron microscope is used, the minimum electron energy required is about:
In the fission of one part of uranium, if 0.5 gm mass is decayed, then how much energy (in kWh) will be obtained?
In a controlled nuclear reactor, the moderator used slows down the neutrons produced due to the fission. The element used as the moderator should be able to
In the reaction given below:
How many α and β particles are emitted?
The nuclei of which one of the following pairs of nuclei are isotones?
In any fission process, the ratio (mass of fission products/mass of parent nucleus)


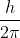 , where h being the Planck's constant. In these orbits, angular momentum of electron can have magnitude as
, where h being the Planck's constant. In these orbits, angular momentum of electron can have magnitude as  , ... etc. but never as
, ... etc. but never as  , ..... etc.
, ..... etc.












