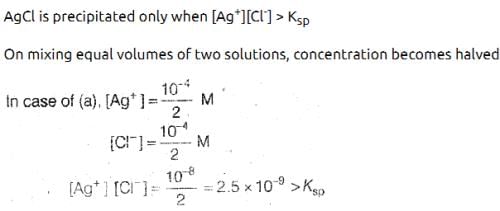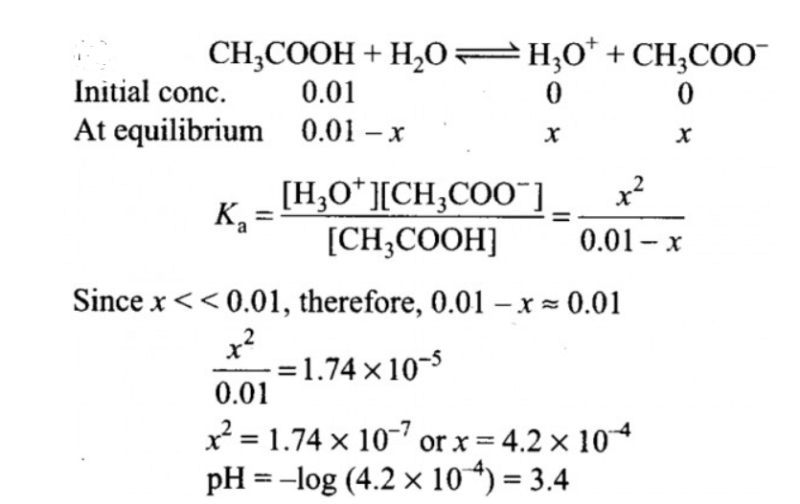Test: Ionic Equilibrium - 1 - SSS 2 MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Ionic Equilibrium - 1
1 c.c. of 0.1N HCl is added to 99 CC solution of NaCl. The pH of the resulting solution will be
10 ml of 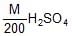 is mixed with 40 ml of
is mixed with 40 ml of 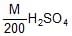 . The pH of the resulting solution is
. The pH of the resulting solution is
The pH of an aqueous solution of 1.0 M solution of a weak monoprotic acid which is 1% ionised is:
If K1 & K2 be first and second ionisation constant of H3PO4 and K1 >> K2 which is incorrect.
What is the percentage hydrolysis of NaCN in N/80 solution when the dissociation constant for HCN is 1.3 × 10-9 and Kw = 1.0 × 10-14
Which of the following solution will have pH close to 1.0 ?
If equilibrium constant of
CH3COOH + H2O CH3COO- + H3O+
Is 1.8 × 10-5, equilibrium constant for
CH3COOH + OH- CH3COO- + H2O is
A solution with pH 2.0 is more acidic than the one with pH 6.0 by a factor of :
The first and second dissociation constants of an acid H2A are 1.0 × 10-5 and 5.0 × 10-10 respectively.
The overall dissociation constant of the acid will be:
An aqueous solution contains 0.01 M RNH2 (Kb= 2 × 10-6) & 10-4 M NaOH.
The concentration of OH- is nearly:
The pKa of a weak acid, HA, is 4.80. The pKb of a weak base, BOH, is 4.78. The pH of an aqueous solution of the corresponding salt, BA, will be:
How many gm of solid NaOH must be added to 100 ml of a buffer solution which is 0.1 M each w.r.t. Acid HA and salt Na+ A- to make the pH of solution 5.5. Given pKa(HA) = 5 (Use antilog (0.5)= 3.16)
If Ksp for HgSO4 is 6.4 × 10-5, then solubility of this substance in mole per m3 is
pH of saturated solution of silver salt of monobasic acid HA is found to be 9.
Find the Ksp of sparingly soluble salt Ag A(s).
Given : Ka(HA) = 10-10
When equal volumes of the following solutions are mixed, precipitation of AgCl (Ksp = 1.8 × 10-10) will occur only with:
If the value of the solubility product for AgBr is 4.0 x 10-12 at 25°C, calculate the solubility of AgBr(s) in water.
For HF, pKa = 3.45. What is the pH of an aqueous buffer solution that is 0.1M HF (aq) and 0.300 M KF (aq)?
What will be the value of pH of 0.01 mol dm–3 CH3COOH (Ka = 1.74 × 10–5)?
For A- + H2O ⇔ HA + OH-, Kb = 1 x 10-12
Thus, pKa of HA + H2O ⇔ H3O+ + A- is ........