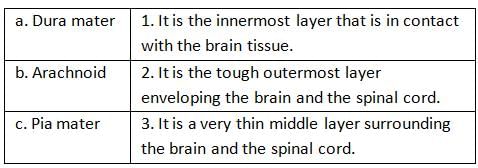
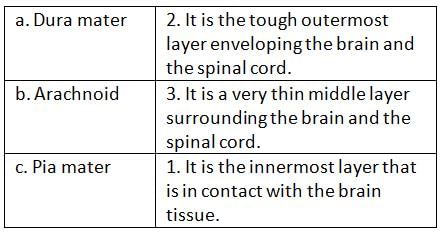
Test: The Functions of Brain & Spinal Cord - JAMB MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: The Functions of Brain & Spinal Cord
Voluntary activities of body are controlled by :-
Which of the following contains cardiovascular reflexes, gastric secretions and the centres that control respiration?
Respiratory control in brain occurs in :-
Which part of the brain regulates the body temperature, hunger and water balance :-
Which of the following is responsible for control of reflex actions :-
Which of the following statements is correct about a resting neuron?
I. Synaptic cleft of neurons secretes adrenaline.
II. Myelinated nerve fibres are enveloped with Schwann cells, which form a myelin sheath around the axon.
III. Non-myelinated nerve fibre is enclosed by a Schwann cell that does not form a myelin sheath.
IV. Spinal cord and cranial nerves are made of non-myelinated nerve fibres.
Which of the following options is true for the above given statements?
Receptor sites for neurotransmitters are present on:
Afferent neurons carry nerve impulses from
Most of the involuntary action are controlled by :-
If cerebellum of man gets damaged, his movement become :-
When the medulla oblongata (M.O.) is compressed, then what happen ?
Cerebral hemisphere is the centre of :- [RPMT–2003]
Which part of brain controls emotions like love, anger and pleasure –
All are the functions of M.O., except :-
Which of the following parts of the brain controls the body temperature and urge of eating?
What is the primary function of afferent nerve fibers in the peripheral nervous system?
What are the two main types of synapses that transmit nerve impulses between neurons?