Test: Reaction Mechanism of Haloalkanes & Haloarenes - JEE MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Reaction Mechanism of Haloalkanes & Haloarenes
Read the following road map carefully
A compond A has the molecular formula C5H9CI. It does not react with bromine in crabon tetrachloride. On treatement with strong base it produces a single compound B. B shas a molecular formula C5H8 and reacts with bromine in carbon tetrachloride. ozonolysis of B produces a compound cC which has a molecular formula C5H8O2. Which of the following structures is that of A?
Which of the following statement is correct
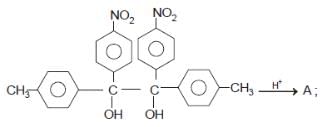
In the reaction 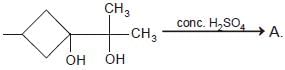 The product is -
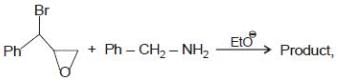
The product is -
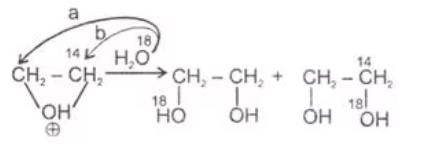
The products of hydrolysis of
(CH3)3CCI + (CH3)3CO–K+ → Product
Neopentyl iodide is treated with aq. AgNO3 solution, a yellow precipitate is formed along with other compound which is
The major end product of the following reaction is
The product of following reacting is
Which can not be the product
The correct order of SN2 E2 ration for the % yield of product of the following halide is
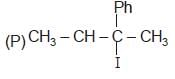
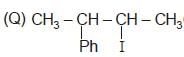
(R) CH3 — CH2 — I
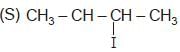
The poduct in the given reaction is
In the reaction mechanism of haloalkanes, a primary haloalkane undergoes nucleophilic substitution via an SN2 pathway. Which of the following statements about the SN2 mechanism is correct?



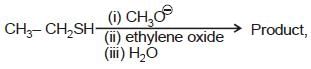
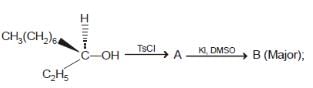
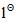 we get 'R' configuration
we get 'R' configuration