Test: MET (Old NCERT) - JEE MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: MET (Old NCERT)
Match the column (I) and (II) and select the correct answer using the codes given below.


NaCN is sometimes added in the froth floatation process as a depressant when mineral contains ZnS and PbS because,
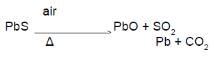
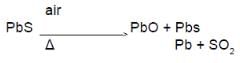
Main source of lead is galena (PbS). It is converted to Pb by :
(A) :
(B)
For which of the following metals Bessemerisation process is important?
I : Fe, II : Cu, III : Al, IV : Silver :
The chemical processes in the production of steel from haematite ore involve:
The chemical composition of 'slag' formed during the smelting process in the extraction of copper is
Which of the following statement is incorrect about the extractive metallurgy of copper?
Which of the following process is used in the extractive metallurgy of magnesium?
Statement-1 : The reduction of a metal oxide is easier if the metal formed is in liquid state at the temperature of reduction.
Statement-2 : The value of entropy change +S of the reduction process is more on +ve side when the metal formed is in liquid state and the metal oxide being reduced is in solid state. Thus the value of +Go becomes more on negative side.
Statement- 1: Extraction of gold from its native ore involves leaching the metal with dilute solution of NaCN in presence of air.
Statement-2 : This is an oxidation reaction and leads to the formation of a soluble comoplex.
Statement- 1: Silica is added as a flux in reverberatory furnace, in the extraction of copper from copper pyrites.
Statement-2 : Silica decreases the melting point of the ore and remove the impurity of lead sulphide as PbSiO3.
Statement- 1: Cast iron is different from pig iron.
Statement-2 : Cast iron is made by melting pig iron with scrap iron and coke using hot air blast and has about 3% carbon content.
Statement- 1: In the Hoop’s process of aluminium purification, the fused materials remain in three different layers. These layers remain intact even in electrolytic reduction.
Statement-2 : This is an oxidation reaction and leads to the formation of a soluble complex.