Test: Ionic Equation - NEET MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Ionic Equation
The degree of dissociation of water in a 0.1 M aqueous solution of HC1 at a cedain temperature t°C is 3.6 x 10-15. The temperature t must be :
Which one is the correct expression below for the solution containing 'n' number of weak acids?
The pH of glycine at the first half equivalence point is 2.34 and that at second half equivalence paint is 9.60. At the equivalence point (The first inflection point) The pH is :
The pK, of a weak acid if titration progress is monitored as follows

A 1.458 g of Mg reacts with 80.0 ml of a HCI solution whose pH is -0.477. The change in pH after all Mg has reacted. (Assume constant volume. Mg = 24.3 g/mol.)(log 3 = 0.477)
Equal volume of two solution having pH = 2 and pH = 10 are mixed together at 90°C. Then pH of resulting solution is : (Take Kw at 90°C = 10-12)
Find the ApH(initial pH -final pH) when 100 ml 0.01 M HCI is added in a solution containig 0.1 m moles of NaHCO3 solution of negligible volume ( Kai =10-7, Ka, =10-11 for H2CO3) :
The ionization constant of benzoic acid is 6.46 x 10-5 and lc for silver benzoate is 2.5 x 10-13. How many times silver benzoate more soluble in a buffer of pH = 3.19 as compared to its solubility in pure water?
30 ml of 0.06 M solution of the protonated form of an anion acid methonine (H2A+) is treated with 0.09 M NaOH. Calculate pH after addition of 20 ml of base. pKa, = 2.28 and pKa2 = 9.2.
A certain acid-base indicator is red in acid solution and blue in basic solution 75% of the indicator is present in the solution in its blue form at pH = 5. Calculate the pH at which the indicator shows 90% red form?
Ionisation constant of HA (weak acid) and BOH (weak base) are 3.0 x 10-7 each at 298K. The percent degree of hydrolysis of BA at the dilution of 10L is :-
Which of the following concentrations of NH4+ will be sufficient to prevent the precipitation of Mg(OH)2 from a solution which is 0.01 M MgCl2 and 0.1 M NH3 (aq).
Given that : K5 of Mg (OH)2 = 2.5 x 10-11 and Kb for NH3(aq) = 2 x 10-6.
Calculate the molar solubility of zinc tetrathiocyanato-N-mercurate (II) if its Ksp = 2.2 x 10-7.
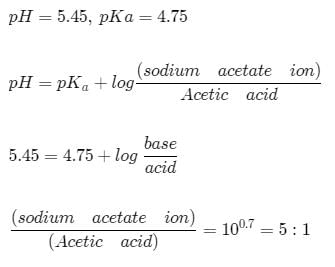
An acid-base indicator which is a weak acid has a pKa value = 5.45. At what cocentration ratio of sodium acetate to acetic acid would the indicator show a colour half-way between those of its acid and conjugate base forms? pKa of acetic acid = 4.75. [log 2 = 0.3]
The indicator constant of phenolphthalein is approximately 10-10. A solution is prepared by adding 100.01 c.c. of 0.01 N sodium hydroxide to 100.00 c.c. of 0.01N hydrochloric acid. If a few drops of phenolphthalein are now added, what fraction of the indicator is converted to its coloured form?
A certain mixture of HCI and CH3 - COOH is 0.1 M in each of the acids. 20 ml of this solution is titrated against 0.1M NaOH. By how many units does the pH change from the start to the stage when the HCI is almpst completely neutralised? Ka for acetic acid = 1.8 x 10-6.
A buffer solution is made by mixing a weak acid HA (Ka = 10-6) with its salt NaA in equal amounts. What should be the amount of acid or salt that should be added to make 90 ml of buffer solution of buffer capacity. 0.1 ?
A sample of water has a hardness expressed as 80 ppm of Ca2+ . This sample is passed through an ion exchange column and the Ca2+ is replaced by H+. What is the pH of the water after it has been so treated? [Atomic mass of Ca = 40]
Statement-1 : solubility of BaSO4 in 0.1 M Na2SO4 is 10-9 M hence its K8 is 10-18.
Statement-2 : because for BaSO4 Ksp = (s)2 [symbols have their usual meanings].
Statement-1 : It is difficult to distinguish the strengths of the strong acids such as HCI, H2SO4, HNO3,HBr, HI or HCIO4 in dilute aqueous solutions.
Statement-2 : In dilute aqueous solution all strong acids donate a proton to water and are essentially. 100% ionised to produce a solution containing H30+ ions plus the anions of strong acid .



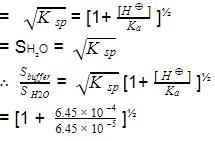
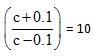
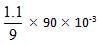 moles = 11 m moles
moles = 11 m moles















