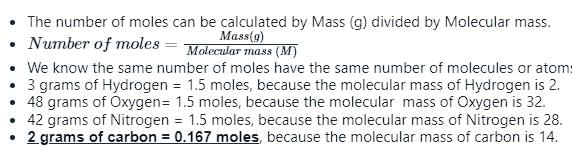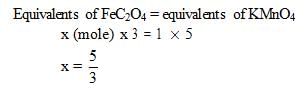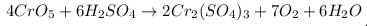Test: Stoichiometry & Stoichiometric Calculations (NCERT) - NEET MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Stoichiometry & Stoichiometric Calculations (NCERT)
What is the correct statement related to Avogadro?
0.16 gm of a dibasic acid required 25 ml of .1N NaOH solution for completed neutralisation. The molecular weight of the acid is
Which one of the following has different number of molecules? (All kept at normal temperature and pressure).
Find the amount of carbon dioxide produced by the combustion of 20g of methane.
What is the amount of water produced when 8g of hydrogen is reacted with 32g of oxygen?
The equivalent mass of H3BO3 (M = Molar mass of H3BO3) in its reaction with NaOH to from Na2B4O7 is equal to –
X gram of pure As2S3 is completely oxidised to respective highest oxidation states by 50 ml of 0.1 M hot acidified KMnO4 then x mass of As2S3 taken is : (Molar mass of As2S3 = 246)
The number of moles of ferrous oxalate oxidised by one mole of KMnO4 is
How many moles of KMnO4 are needed a mixture of 1 mole of each FeSO4 & FeC2O4 in acidic medium
In the reaction
Na2S2O3 + 4C12 + 5H2O → Na2SO4 + H2S04 + 8HCI
the equivalent weight of Na2 S2 O3 will be
(M= molecular weight of Na2S2O3)
C2H4 + xO2 -> 2CO2 + yH2O, what is the value of x + y?
The following equations are balanced atomwise and chargewise.
(i) Cr2O72- + 8H+ + 2H2O2 → 2Cr3+ + 7H2O + 2O2
(ii) Cr2O72- + 8H+ + 5H2O2→ 2Cr3+ + 9H2O + 4O2
(iii) Cr2O72- + 8H+ + 7H2O2→ 2Cr+ + 11H2O + 5O2
The precise equationl equations representing the oxidation of H2O2 is/are
An excess of NaOH was added to 100 mL of a ferric chloride solution. This caused the precipitation of 1,425 g of Fe(OH)3. Calculate the normality of the ferric chloride solution
In the reaction CrO5 + H2SO4 →Cr2(SO4)3 + H2O + O2 one mole of CrO5 will liberate how many moles of O2
0.4g of a polybasic acid HnA (all the hydrogens are acidic) requires 0.5g of NaOH for complete neutralization. The number of replaceable hydrogen atoms in the acid and the molecular weight of 'A' would be : (Molecular weight of the acid is 96 gms.)
A solution of Na2S2O3 is standardized iodimetrically against 0.1262 g of Mr% This process requires 45 mL of the Na2 S203 solution. What is the strength of the Na2S2O3?
25.0 g of FeSO4.7H2O was dissolved in water containing dilute H2SO4, and the volume was made up to 1.0 L. 25.0 mL of this solution required 20 mL of an N/10 KMnO4 solution for complete oxidation. The percentage of FeSO4. 7H2O in the acid solution is
1.0 mol of Fe reacts completely with 0.65 mol of O2 to give a mixture of only Fe0 and Fe2O3. The mole ratio of ferrous oxide to ferric oxide is
25 mL of a solution containing HCf and H2S04 required 10 mL of a 1 N NaOH solution for neutralization. 20 mL of the same acid mixture on being treated with an excess of AgNO3 gives 0.1425 g of AgCf. The normality of the HC and the normality of the H2S04 are respectively
If 10 gm of V2O5 is dissolved in acid and is reduced to V2+ by zinc metal, how many mole of I2 could be reduced by the resulting solution if it is further oxidised to VO2+ ions ?
[Assume no change in state of Zn2+ions] (V = 51, 0 = 16, I = 127) :
0.70 g of mixture (NH4)2 SO4 was boiled with 100 mL of 0.2 N NaOH solution till all the NH3(g) evolved and get dissolved in solution itself. The remaining solution was diluted to 250 mL. 25 mL of this solution was neutralized using 10 mL of a 0.1 N H2SO4 solution. The percentage purity of the (NH4)2 SO sample is
A mixed solution of potassium hydroxide and sodium carbonate required 15 mL. of an N/20 HCI solution when titrated with phenolphthalein as an indicator. But the same amount of the solution when titrated with methyl orange as an indicator required 25 mL of the same acid. The amount of KOH present in the solution is
The percentage of copper in a copper(II) salt can be determined by using a thiosulphate titration. 0.305 gm of a copper(II) salt was dissolved in water and added to, an excess of potassium iodide solution liberating iodine according to the following equation
2Cu2 (aq) + 4I– (aq) 2CuI(s) + I2(aq)
The iodine liberated required 24.5cm3 of a 0.100 mole dm-3 solution of sodium thiosulphate
2S2032- (aq) + I2(aq) → 2I– (aq) + S4062- (aq)
the percentage of copper, by mass in the copper (ll) salt is. [Atomic mass of copper = 63.5]
KIO3 reacts with KI to liberate iodine and liberated Iodine is titrated with standard hypo solution, The reactions are
1. IO3– + I– →I2 (valency factor = 5/3)
2. I2 + S2O32– → S4O62– + I– (valency factor = 2)
meq of hypo = meq of I2 = meq of IO3– + meq of I–
IO3– react with I– ⇒ meq of IO3– = meq of I–
Statement-1 : meq of hypo = 2 x meq of IO3–
Statement-2 : valency factor of I2 in both the equation are different therefore we cannot equate milliequivalents in sequence
In the reaction:
2 C2H6 + 7 O2 → 4 CO2 + 6 H2O
how many moles of CO2 are formed when 1 mole of O2 is consumed?