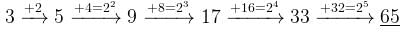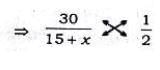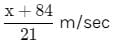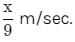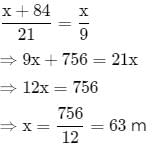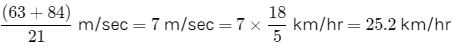Test: Quantitative Techniques- 3 - CLAT MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Quantitative Techniques- 3
If one-ninth of a certain number exceeds its one-tenth by 4, the number is
A coin is tossed thrice. The probability that exactly two heads show up is
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The angles of a triangle are in the ratio 3 : 4 : 5. The measure of the largest angle of the triangle is
The sum of three numbers is 98. If the ratio of the first to the second is 2 : 3 and that of the second to the third is 5 : 8, then the second number is
If the circumference of a circle is reduced by 50%, its area will be reduced by
12 persons can do a piece of work in 4 days. How many persons are required to complete 8 times the work in half the time?
Two pipes can fill a tank in 15 hours and 20 hours respectively, while the third can empty it in 30 hours. If all the pipes are opened simultaneously, the empty tank will be filled in
The next number of the sequence 3, 5, 9, 17, 33, …….is
The cost price of 8 articles is equal to the selling price of 9 articles. The profit or loss per cent in the transaction is
If 78*3945 is divisible by 11. where * is a digit, then * is equal to
In a 45 litres mixture of milk and water, the ratio of the milk to water is 2 : 1. When some quantity of water is added to the mixture, this ratio becomes 1 : 2. The quantity of water added is
A and B together can do a piece of work in 10 days. A alone can do it in 30 days. The time in which B alone can do it is
If the price of tea is increased by 20%, by how much per cent the consumption of tea be reduced so that there is no increase in the expenditure on it?
The smallest 4-digit number, which is a perfect square, is
The difference between a single discount of 30% on Rs. 550 and two successive discounts of 20% and 10% on the same amount is
A dealer makes a profit of 20% even after giving a 10% discount on the advertised price of a scooter. If he makes a profit of Rs. 7500 on the sale of the scooter, the advertised price was
A person standing on a railway platform noticed that a train took 21 seconds to completely pass through the platform which was 84 m long and it took 9 seconds in passing him. The speed of the train was
The average of runs scored by a player in 10 innings is 50. How many runs should he score in the 11th innings so that his average is increased by 2 runs?



 Reduction in area = πr2−πr2/4 =3πr2/4
Reduction in area = πr2−πr2/4 =3πr2/4