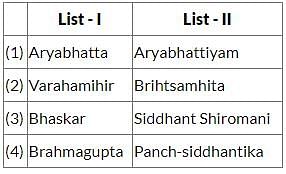
UPPSC Prelims (GS I) Mock Test - 1 - UPPSC (UP) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - UPPSC Prelims (GS I) Mock Test - 1
According to the Census of 2011, what percentage of the total population of the whole country lives in Uttar Pradesh?
Which of the following continent, in which tropic of cancer, equator and tropic of capricorn passes through?
Mauryan government kept control of marketing system and appointed official who checked the malpractice in trade. These were known as:
Which Islamic reformist movement was founded by Mirza Gulam Ahmad?
Consider the following statements regarding the 73rd Constitutional Amendment Act of 1992:
- It provided provisions for the reservation of seats for women, SC, ST candidates only in Rural Panchayat bodies.
- State can authorise a Panchayat to levy, collect taxes, duties, tolls etc.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
In which of the following relief sculpture inscriptions is 'Ranyo Ashoka' (Kind Ashoka) mentioned along with the stone portrait of Ashoka?
Consider the following statements about Karewas:
- These are the lacustrine deposits of Pleistocene period.
- These are found along the lower slopes of Pir Panjal.
- Karewas are well known for the cultivation of saffron, almond and walnut.
How many of the above statements is/are correct?
Consider the following statements.
- Right to cast a vote in elections is neither a fundamental right nor a right under common law.
- Prisoners can cast their vote from jails through postal ballot.
Which of the above statements is/are incorrect?
Which part of the Constitution of India declares the ideal of Welfare State?
Reproduction cannot be an all-inclusive defining characteristic feature of living organisms because:
The plant disease "Late Blight of Potato" is caused by which of the following organism?
Which of the following is not a Fundamental Duty mentioned under the Indian Constitution?
Consider the following:
- Establishment of the High Courts at all Presidencies.
- Bhutan War
- Treaty of Sinchula was signed.
The events given above took place during the tenure of which among the following Viceroy?
Who was the Delhi Sultan who imposed a tax on Brahmins?
Arrange the following states in the correct order from highest to lowest sex ratio as per 2011 census of India.
I. Nagaland
II. Rajasthan
III. Jharkhand
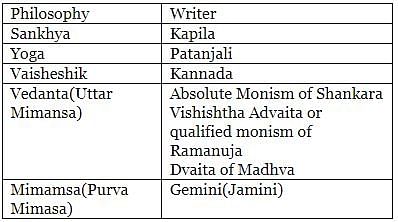
Vedic Sage Kapila belonged to _________ school of Indian philosophy.
Which of the following is NOT an example of small savings?
What percentage of the total population of Uttar Pradesh resides in villages?
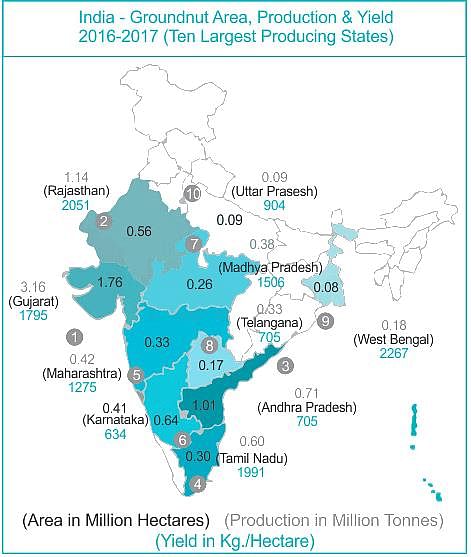
Which of the following are the varieties of groundnut?
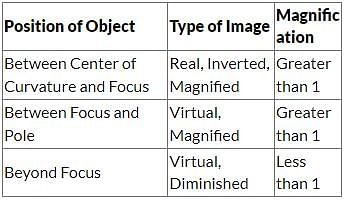
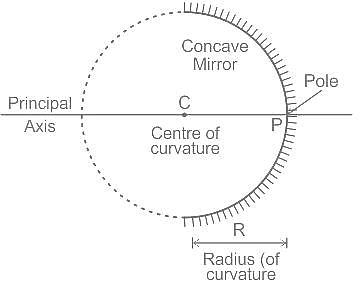
Where should an object be placed in front of a concave mirror such that the image of the object is of the same size as the object?
Where did Subhas Chandra Bose establish the Provisional Government of Free India?
Which of the following industries should have the compulsory licensing?
What was a key outcome of Uttar Pradesh surpassing Gujarat in registered investors?
What is the expected impact of the Ram temple inauguration on tourism in Ayodhya?
Which region in Uttar Pradesh accounts for nearly 60% of the total solar energy generated in the state?