Software Development Exam > Software Development Tests > Test: Physical World - Software Development MCQ
Test: Physical World - Software Development MCQ
Test Description
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Physical World
Test: Physical World for Software Development 2025 is part of Software Development preparation. The Test: Physical World questions and answers have been prepared
according to the Software Development exam syllabus.The Test: Physical World MCQs are made for Software Development 2025 Exam.
Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Test: Physical World below.
Solutions of Test: Physical World questions in English are available as part of our course for Software Development & Test: Physical World solutions in
Hindi for Software Development course.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Software Development Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Test: Physical World | 10 questions in 12 minutes | Mock test for Software Development preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study for Software Development Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Detailed Solution for Test: Physical World - Question 1
Detailed Solution for Test: Physical World - Question 2
Test: Physical World - Question 3
Which of the following quantities can be zero for a body while it is in motion?
Detailed Solution for Test: Physical World - Question 3
Detailed Solution for Test: Physical World - Question 4
Test: Physical World - Question 5
Calculate the acceleration produced when a force of 100 N is applied to an object of mass 50 kg.
Detailed Solution for Test: Physical World - Question 5
Test: Physical World - Question 6
A boy raises a box with a weight of 120 N from a height of 2 m. The work done by him is ________.
Detailed Solution for Test: Physical World - Question 6
Test: Physical World - Question 7
If a man takes an object of 80 kg weight to a certain height in time 12 sec and another man takes an object of 60 kg weight to the same height in 11 sec, then find the ratio of the power
Detailed Solution for Test: Physical World - Question 7
Detailed Solution for Test: Physical World - Question 8
Test: Physical World - Question 9
If G is the gravitational constant and g is the acceleration due to gravity, the unit of G/g is
Detailed Solution for Test: Physical World - Question 9
Test: Physical World - Question 10
What is the value of acceleration due to the gravity of the surface of the Earth?
Detailed Solution for Test: Physical World - Question 10
Information about Test: Physical World Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Test: Physical World solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Test: Physical World, EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice
Download as PDF



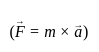
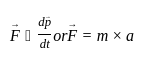
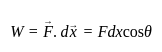
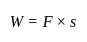
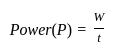
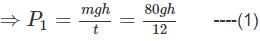
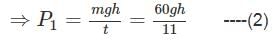

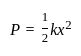
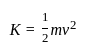
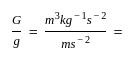 kg-1 m2
kg-1 m2
















