KTET Paper 2: Science and Mathematics Test - 2 - KTET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - KTET Paper 2: Science and Mathematics Test - 2
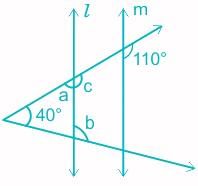
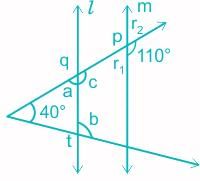
In the following figure, if l || m, then find the measures of angles marked by a and b.

Following are some questions posed by the teacher in the mathematics classroom:
A. What shall be added to 3 to get 5?
B. Give any two numbers whose subtraction is 5.
C. Write any four numbers greater than 5.
D. Which of the following is greater than 3.4?
A. What shall be added to 3 to get 5?
B. Give any two numbers whose subtraction is 5.
C. Write any four numbers greater than 5.
D. Which of the following is greater than 3.4?
The mean of 10 numbers is 0. If 72 and -12 are also added to these numbers, the new mean will be
A star has a diameter of approximately 0.5 that of the earth and mass of 0.1 that of the earth. The force experienced by a body of mass 1 kg on the surface of that star is what times to that experienced on the earth's surface?
A student obtained a total of 630 marks in 5 subjects in an examination. Marks obtained in Hindi, English, Mathematics, Science and Social Science when shown in a pie chart by making central angles 65°, 53°, 85° 81° and 76° respectively. How many more marks were obtained by the student in Mathematics than in Science ?
If x2 + (2x/5) + (1/25) = 0, then (x−(2/3))2 = ?
If the rational numbers 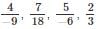 are arranged in ascending order, which of the following will be placed first?
are arranged in ascending order, which of the following will be placed first?
An adaptation seen in the camel is that it can close its nostril. This helps to prevent ________.
If 'x' is an integer, then (x + 1)4 – (x – 1)4 is always divisible by
To represent equal numerical values, same type of diagrams are used in
The deficiency of copper in a body causes which of the following diseases?
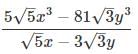 = Ax2 + By2 + Cxy, then find the value of 16A + B - √15C?
= Ax2 + By2 + Cxy, then find the value of 16A + B - √15C?
Direction: Answer the following questions by selecting the correct / most appropriate options.
Statement A): Desert Oak is a desert plant.
Statement B): It has adaptations to reduce the water lost due to evapotranspiration.
A car goes one kilometre at 30 km per hour and then goes another kilometre at 40 km per hour. The average speed (in km/hr) of the car for 2 km is
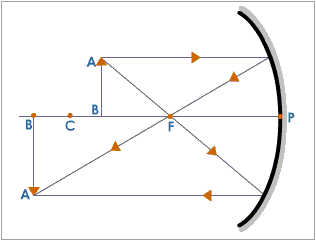
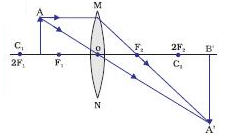
You are provided with a concave mirror, a concave lens, a convex mirror and a convex lens. To obtain an enlarged image of an object, you can use either
Three positive numbers are in the ratio 2 ∶ 3 ∶ 4. The sum of their squares is 2349. The average of the first two numbers is:
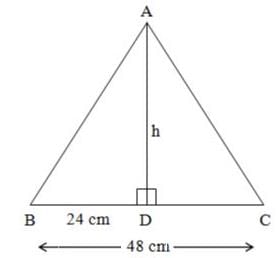
If the base of an isosceles ΔABC is 48 cm and its area is 168 cm2, then what is the length of one of its equal sides?
A task assigned to the class Vlll student is as follows:
An open box is to be made out of a metallic sheet of 50 cm x 65 cm. Length and breadth of the box is 30 cm and 15 cm, respectively. What is the possible height of the box? Also find the volume of this box.
This task refer to
Correlation of which of the following mathematical principles is reflected in the construction of the monument, Taj Mahal?
"Audio visual aids are those sensory objects or images which initiate or stimulate and reinforce learning" is said by whom?
If a learner is able to perform the four basic operations on whole numbers, fractions and decimal numbers, the learner is at _________.
A science teacher wants to teach the topic of Biodiversity to the students. The best way of teaching, she should adopt:
If 2460375= 3375 × 729, then the cube root of 2460375 is:
A teacher in class 5th provided each child with a centimeter grid paper and a pair of scissors. She wanted to teach them to explore how two dimensions shapes can be folded into three dimensional objects. Which of the following concepts are the students exploring:
Which among the following statements is correctly describing the relationship between science and technology?
As per NCF 2005, Mathematics curriculum is ambitious, coherent and teaches important Mathematics. Here, 'ambitious' refers to
A tightly structured lesson of Physics if taught with little flexibility is least conducive to the learning of the student who
The difference between supplementary and complementary angles of any given acute angle is:
Fill in the gaps:
_____ ÷ _____ = 4
What type of question is it?
At the beginning stage of learning Mathematics, what should the child learn?



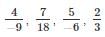
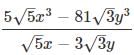 = Ax2 + By2 + Cxy
= Ax2 + By2 + Cxy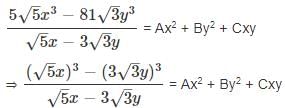
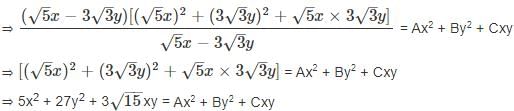
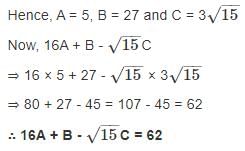

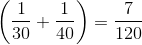 hrs
hrs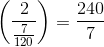 km/hr =
km/hr = 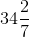 km/hr
km/hr