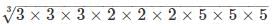KTET Paper 2: Science and Mathematics Test - 4 - KTET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - KTET Paper 2: Science and Mathematics Test - 4
Which one of the following expressions is equal to (3x - 5) ?
If a variable takes discrete values a + 4, a - 3.5, a - 2.5, a - 3, a - 2, a + 0.5, a + 5 and a - 0.5 where a > 0, then the median of the data set is
A teacher asks the grade two students to tell about the number of pockets are there in each child's dress. Which mode of visual representation will be the best suited for this age group?
If a2 - 3a + 1 = 0 and a ≠ 0, then the value of a + (1/a) is
Some dinosaurs had feathers although they could not fly, but birds have feathers that help them to fly. In the context of evolution this means that
What is the S.I. unit of potential difference?
The base of a right prism is a trapezium whose parallel sides are 11 cm and 15 cm and the distance between them is 9 cm. If the volume of the prism is 1614.6 cm3, then the height (in cm) of the prism is:
If 32400 = 2p × 3q × 5r where p, q and r are the natural numbers then what is the value of 2pq + 3qr ?
Which among the following is used for preserving food?
a. Sugar
b. Vinegar
c. Common Salt
How can 0.33 ÷ 0.11 be expressed as a percentage?
A cricket ball's cost is Rs. 36 and the cost of a cricket bat is 12(1/2) times that of the cost of the cricket ball. What is the cost of the cricket bat (in rupees)?
The image of a distant coloured object formed in a pinhole camera is always
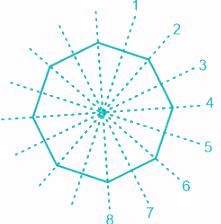
Assertion(A): An regular octagon has 8 lines of symmetry.
Reason (R): The number of lines of symmetry of a regular polygon is equal to the number of its sides.
Which of the following is correct?
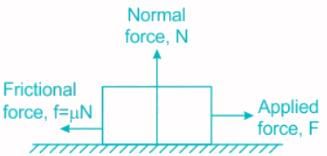
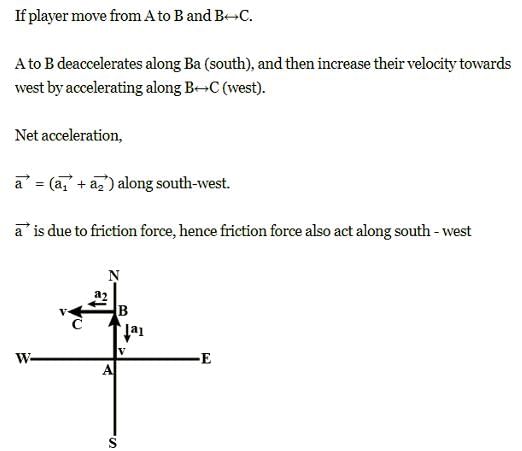
A hockey player is moving northward and suddenly turns westward with the same speed to avoid an opponent. The force that acts on the player is
Natural numbers 4 to 15 are written on different slips (one number on one slip), kept in a box and mixed well. Renu picks up one slip from the box without looking into it. What is the probability that this slip bears a prime number?
The atoms 6C13 and 7N14 can be described as
The sum of the digits of the minimum number by which 1800 is multiplied to get a perfect cube number is :
The length, breadth, and height of the cuboidal room are 13 m, 12 m, and 15 m respectively. What is the cost of whitewashing the four walls of the room if the cost of whitewashing is Rs. 9 per m2?
Which of the following assessment strategies can be used to make connections of mathematics with real life and promote interdisciplinary?
One of the main limitations of the project method of teaching science is that :
While teaching 'Polynomials', a good teacher asked the students to prepare for a project on the topic. The aim of the teacher was
'Learning by doing' is the concept of which of the following?
The project method of teaching is best associated with the philosophy of
A phase named 'Zone of Proximal Development (ZPD)' is a part of the strategy of
In the preparation of the Herbartian lesson plan, the stage after generalisation is
While analysing class VIII biological science textbook by using Hunter's Score Card, percentages of weightage given to content and author's educational level are ___________, respectively.
Which one of the following statements is correct?
A which stage the child should be engaged in learning principles of science through familiar experiences, working with hands to design simple technological units and modules (e.g. designing and making a working model of a windmill to lift weights) and continuing to learn more on environment and health through activities and surveys?
The ratio of two numbers is 5 ∶ 6. The product of their HCF and LCM is 270, then find the sum of the numbers.
As per NCF 2005, Mathematics curriculum is ambitious, coherent and teaches important Mathematics. What does 'ambitious' here refer to?