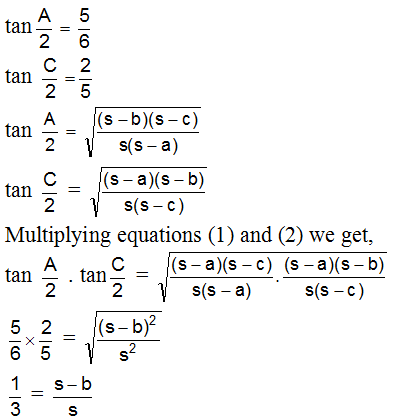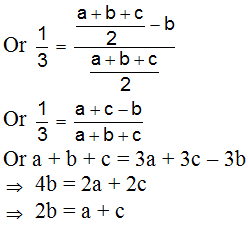KTET Paper 2: Science and Mathematics Test - 8 - KTET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - KTET Paper 2: Science and Mathematics Test - 8
The diagonal of a rectangle is 17 cm and its area is 120 cm2. The perimeter of the rectangle is ____
Which of the following(s) is/are the skill of micro-teaching in Mathematics?
i. skill of integrating knowledge and experience
ii. skill of facilitating child-centric learning
iii. skill of developing observation in learners
i. skill of integrating knowledge and experience
ii. skill of facilitating child-centric learning
iii. skill of developing observation in learners
Which of the following statement is/are correct?
S1 - Average speed of an object over a finite interval of time is greater than or equal to the magnitude of average velocity.
S2 - Instantaneous speed at any instant is equal to the magnitude of instantaneous velocity.
S1 - Average speed of an object over a finite interval of time is greater than or equal to the magnitude of average velocity.
S2 - Instantaneous speed at any instant is equal to the magnitude of instantaneous velocity.
When we add aluminium foil to freshly prepared sodium hydroxide solution, a gas is produced. Which of the following correctly states the property of this gas?
The taste buds for bitter taste are present at the
Find the remainder when 8317+5217+8417+5317 is divided by 68.
Which of the following statements is/are true?
1. If a body does not change its position as time passes it is at rest.
2. There is no meaning of rest or motion without the viewer.
Choose the correct code.
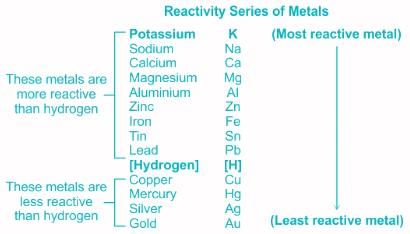
Arrange the following metals in the increasing order of their reactivity towards water :
I. Zinc
II. Iron
III. Magnesium
IV. Sodium
Two numbers are in the ratio 3 : 5. If 9 is subtracted from each, the new numbers are in the ratio 12 : 23. The smaller number is
Human ear can hear two sounds separately if the minimum time interval (T) between the two sounds is
Which of the following options represents a set of Kharif crops?
If 20 percent of P is added to 40 percent of Q, then the resultant comes as 80 percent of Q. P is what percentage of Q?
A cold steel spoon is dipped in a cup of hot milk, then its other end -
If the velocity-time graph of particle is represented by y=mt, then the particle is moving with
3 x 105 + 4 x 103 + 7 x 102 + 5 is equal to
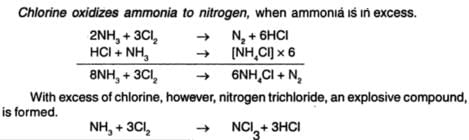
Ammonia reacts with excess of chlorine to form an explosive compound 'X'. The compound 'X' is
You have phenolphthalein solution in three test tubes A, B and C. On putting 2-3 drops of dilute hydrochloric acid in A, a solution of sodium hydroxide in B and distilled water in C, if you immediately observe the colour of the solution in each test tube, you will find that the solution in the test tube
Raghav can split and recombine fractions mentally to add or subtract as
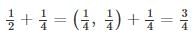
In which developmental stage of numbers does Raghav lies?
Which of the following is not a mineral acid?
In a mathematics classroom, emphasis is placed on
The teaching-learning process of Science in a classroom at any level of formal education is directed by
The topic 'Separation of Substances' in Class VI can be taught most effectively by
Mathematics helped man to discover the mysteries of nature and to overcome superstitions and ignorance. This shows the
The bacteria responsible for fermentation of dairy milk and plant product are
How can we say science is always tentative?
Characteristic of simplicity relates to which of the following?
"Science is the investigation and interpretation of events or phenomenon that occurs in natural environment and within our own body."
The above-mentioned definition of Science is given by
Which of the following questions would be an 'open-ended' question?



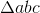 , tan
, tan 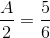 , tan
, tan 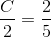 , then
, then