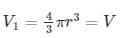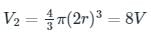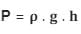Test: Pascal's Principle - 1 - EmSAT Achieve MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Pascal's Principle - 1
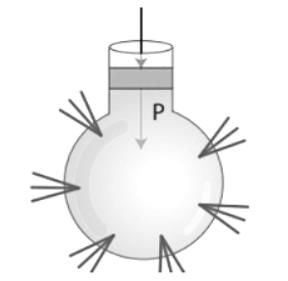
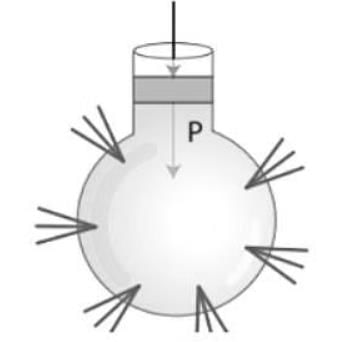
A glass bottle filled with liquid will break at the bottom if a stopper is forced into its open end as per
A stream of water flowing horizontally with a speed of 20 m/s pushes out of a tube of cross-sectional area 10-1m2 and hits at a vertical wall nearby. Find the force exerted on the wall by the impact of water, assuming that it does not rebound?
A liquid is filled in a large cylindrical container. The pressure exerted by the liquid on the wall of the container depends on
At what depth from surface of water, the pressure will be equal to three times the atmosphere pressure? Given atmospheric pressure = 10 N/cm2 and g = 9.8 m/s2.
The resultant pressure on a body submerged in a fluid due to the fluid acts at which of the following points in the body?
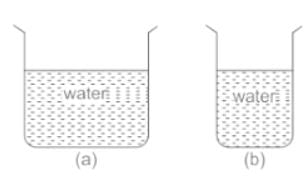
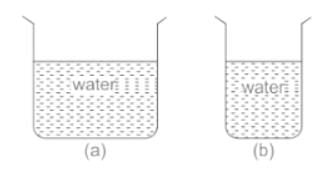
From the adjacent figure, the correct observation is ______
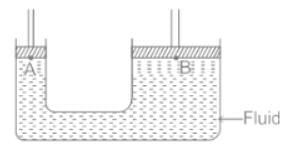
A hydraulic lift has two pistons with area 1 m2 and 0.25 m2. What is the force exerted by the smaller piston when 40 N is placed on the larger piston?
An air bubble of radius 'r' doubles its radius as it rises from a depth 'h' to the surface of the lake at a constant temperature. If the atmospheric pressure is equal to 10 m height of the water column, neglecting surface tension the value of 'h' is:
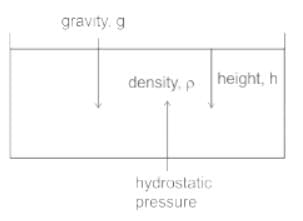
The pressure exerted by a liquid column at the bottom of the liquid container is