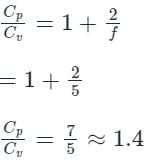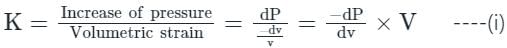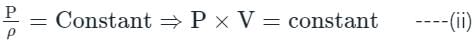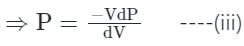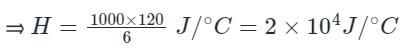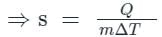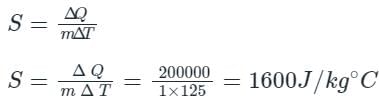Test: Specific Heat Capacity - EmSAT Achieve MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Specific Heat Capacity
The sprinkling of water reduces slightly the temperature of a closed room because:
A metal ball of mass 0.5 kg falls freely from a height of 10 m and bounces to a height of 5.5 m from the ground. If the dissipated energy in this process is absorbed by the ball, the rise in its temperature is?
(Specific heat of metal = 450J/Kg°C )
Which of the following statements about specific heat of a body is/are correct?
- It depends upon mass and shape of the body
- It is independent of mass and shape of the body
- It depends only upon the temperature of the body
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
In gases of diatomic molecules, find the ratio of the two specific heat of gases 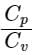 .
.
4 kg of solid material is heated from 15°C to 115°C with the addition of 750 kJ of heat in a furnace. What will be it specific heat?
In the isothermal condition, the isothermal bulk modulus of an ideal gas is equal to ______.
An electric heater of power 1000 W raises the temperature of 5 kg of liquid from 25°C to 31°C in 2 minutes. What is heat capacity of the liquid?
If 'ΔQ' stands for the amount of heat absorbed or rejected by a substance of mass 'm' when it undergoes a temperature change 'ΔT', then "ΔQ / (mΔT)" is equal to ____________.
If 1 kg of wood absorbs 200 kJ of heat energy, and its temperature changes from 25°C to 150°C. In this case, what will be the specific heat of wood?