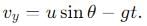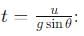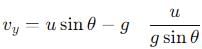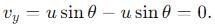Test: Motion in a Plane - 1 - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Motion in a Plane - 1
When a ball is thrown upwards, as it rises, the vertical component of its velocity
The reason why cyclists bank when taking a sharp turn is
A motorcycle stunt rider rides off the edge of a cliff. Just at the edge his velocity is horizontal, with magnitude 9.0 m/s. Find the magnitude of the motorcycle’s position vector after 0.50s it leaves the edge of the cliff.
A sports car has a “lateral acceleration” of 0.96g = 9.4 m s−2. This is the maximum centripetal acceleration the car can sustain without skidding out of a curved path. If the car is traveling at a constant 40 m/s on level ground, what is the radius R of the tightest unbanked curve it can negotiate?
A cyclist moves along a circular path of radius 70m. If he completes one round in 11s, calculate total length of path.
In a harbor, wind is blowing at the speed of 72 km/h and the flag on the mast of a boat anchored in the harbor flutters along the N-E direction. If the boat starts moving at a speed of 51 km/h to the north, what is the direction of the flag on the mast of the boat?
A man can swim with a speed of 4.0 km/h in still water. How long does he take to cross a river 1.0 km wide if the river flows steadily at 3.0 km/h and he makes his strokes normal to the river current? How far down the river does he go when he reaches the other bank?
A ball rolls off top of a staircase with a horizontal velocity u m/s. If the steps are h metre high and b mere wide, the ball will just hit the edge of nth step if n equals to
A man standing on the roof of a house of height h throws one particle vertically downwards and another particle horizontally with the same velocity u. The ratio of their velocities when they reach the earth’s surface will be
Rain is falling vertically with a speed of 30 m s−1. A woman rides a bicycle with a speed of 10 m s−1 in the north to south direction. What is the direction in which she should hold her umbrella?
A man weighing 80 kg is standing in a trolley weighing 320 kg. The trolley is resting on frictionless horizontal rails. If the man starts walking on the trolley with a speed of 1 m/s, then after 4 sec his displacement relative to the ground will be
A particle is projected at an angle θ with horizontal with an initital speed u. When it makes an angle α with horizontal, its speed v is-
A passenger arriving in a new town wishes to go from the station to a hotel located 10 km away on a straight road from the station. A dishonest cabman takes him along a circuitous path 23 km long and reaches the hotel in 28 min. What is (a) the average speed of the taxi, (b) the magnitude of average velocity?
A particle is moving along the path y = x2 from x = 0 m to x = 2 m. Then the distance traveled by the particle is:
A projectile is fired a velocity of 150 meters per second at an angle of 30 degrees with the horizontal. What is the magnitude of the vertical component of the velocity at the time the projectile is fired?
Six particles situated at the corners of a regular hexagon of side a move at constant speed v. Each particle maintains a direction towards the particle at the next. The time which the particles will take to meet each other is:
A body is projected with velocity 20√3 m/s with an angle of projection 60° with horizontal. Calculate velocity on that point where body makes an angle 30° with the horizontal.
We can define the difference of two vectors A and B as the
In a uniform circular motion, which of the following quantity is not constant
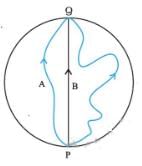
Three girls skating on a circular ice ground of radius 200 m start from a point P on the edge of the ground and reach a point Q diametrically opposite to P following different paths as shown in Figure. What is the magnitude of the displacement vector for each ? For which girl is this equal to the actual length of path skate ?
A particle is moving with veocity 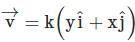 ; where k is constant. The general equation for the path is:
; where k is constant. The general equation for the path is:
A particle is projected with a velocity u making an angle θ with the horizontal. At any instant, its velocity v is at right angles to its initial velocity u; then v is:




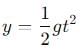
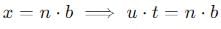
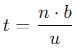
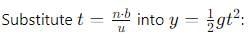
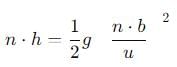
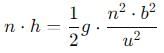
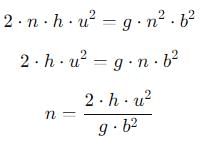
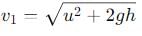
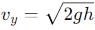
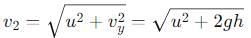
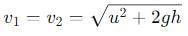
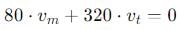
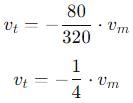
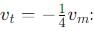
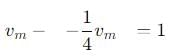
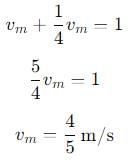
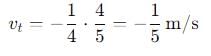
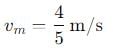
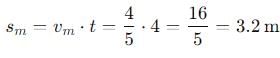
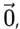 , and its magnitude is given by
, and its magnitude is given by 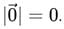 . It plays a fundamental role in vector algebra, serving as the additive identity in vector addition.
. It plays a fundamental role in vector algebra, serving as the additive identity in vector addition.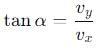
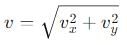
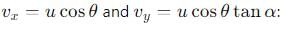
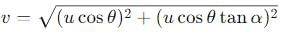
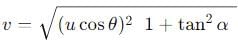
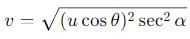
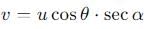
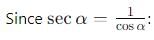
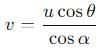
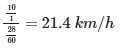
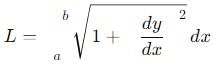
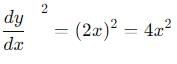
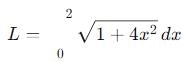
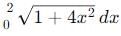 cannot be solved exactly using elementary functions, but its value is slightly greater than
cannot be solved exactly using elementary functions, but its value is slightly greater than 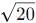 because
because 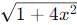 grows faster than
grows faster than 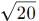 over the interval [0, 2].
over the interval [0, 2].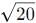 , making Option 3 ( >
, making Option 3 ( > 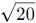 ) the correct choice.
) the correct choice.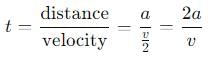
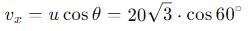
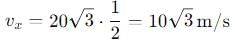
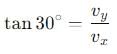
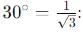
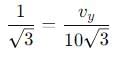
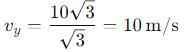
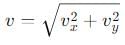
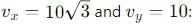
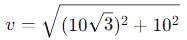
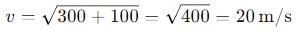
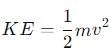
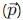 is a vector quantity given by:
is a vector quantity given by: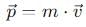
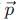 changes continuously as the object moves along the circular path.
changes continuously as the object moves along the circular path.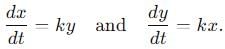
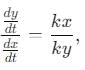
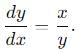
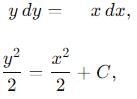
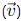 becomes perpendicular to the initial velocity
becomes perpendicular to the initial velocity 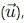 their dot product is zero:
their dot product is zero: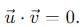
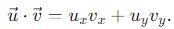
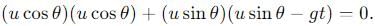
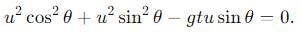
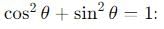
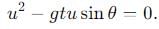
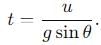
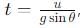 , the vertical velocity is:
, the vertical velocity is: