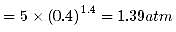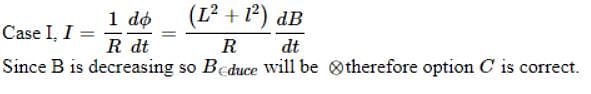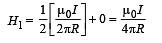KVS PGT Physics Mock Test - 8 - KVS PGT/TGT/PRT MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - KVS PGT Physics Mock Test - 8
In the following question, an idiomatic expression and its four possible meanings are given.
Q. Find out the correct meaning of the idiom.Back to square one.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
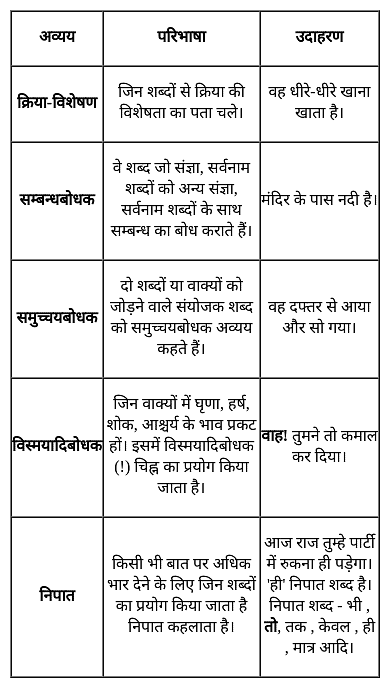
वह लाचार है, क्योंकि वह अंधा है।" इस वाक्य में कौन-सा अव्यय है ?
Which one amongst the subsequent isn't the factor that determines the implementation of a curriculum?
How does peer assessment help students?
I. Organize your learning by talking and interacting with your classmates.
II. Learn how to give and receive constructive, specific feedback based on clear criteria.
Which of the following expression is true for surface tension?
A cube-shaped permanent magnet is made of a ferromagnetic material with a magnetization 500M of about The side length is 20 cm. Magnetic dipole moment of the magnet is.
When is the work done by a conservative force equal to zero?
A block of mass 2 kg is placed on the floor. The coefficient of static friction is 0.4. If a force of 2.8 N is applied on the block parallel to floor, the force of friction between the block and floor is (Take g = 10 m/s2)
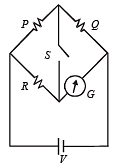
In the circuit P≠R , the reading of the galvanometer is same with switch S open or closed. Then
A child stands at the centre of a turntable with his two arms outstretched. The turntable is set rotating with an angular speed of 40 rpm. How much is the angular speed of the child if he folds his hands back and thereby reduces his moment if inertia to 2/5 times the initial value? Assume that the turntable rotates without friction.
Two moles of an ideal gas (γ=1.4) expands slowly and adiabatically from a pressure of 5.00 atm and a volume of 12.0 L to a final volume of 30.0 L. What is the final pressure of the gas?
Two different arrangements in which two square wire frames of same resistance are placed in a uniform constantly decreasing magnetic field B.
The direction of induced current in the case II is
When does the potential energy of a spring increase?
What happens to the magnifying power of microscope, when its length increases?
An infinitely long conductor PQR is bent to form a right angle as shown in Figure. A current I flows through PQR. The magnetic field due to this current at the point M is H1. Now, another infinitely long straight conductor QS is connected at Q so that current is I/2 in QR as well as in QS, the current in PQ remaining unchanged. The magnetic field at M is now H2. The ratio H1/H2 is given by

A cylinder of radius r and mass m rests on a curved path of radius R as shown in the figure. It is slightly displaced to its left. Thus, the cylinder makes oscillation about the mean position. The period of oscillations is (the cylinder rolls without slipping)
Three identical cells, each of 2V and internal resistance of 0.2 ohm are connected in series to an external resistance of 7.4 ohm. The current in the circuit will be
An object is placed on the surface of a smooth inclined plane of inclination θ It takes time ‘t’ to reach he bottom. If the same object is allowed to slide down a rough inclined plane of inclination θ it takes time nt to reach the bottom where n is a number greater than 1. The coefficient of friction μ is given by
Materials that show very small plastic range beyond elastic limit are called