UGC NET Paper 2 Geography Mock Test - 8 - UGC NET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - UGC NET Paper 2 Geography Mock Test - 8
Which one of the following kinds of towns was not planned and developed during the British Rule in India?
The social theory that appeared as the sequel to Behaviouralism is
Which function of total station is used to determine the heights of inaccessible points where it is not possible to locate the prism?
Which one of the following is not a geographical factor favorable for the location of an industry?
Which of the following is not associated with political Geography
A) I. Bowman
B) R. Johnson
C) F. Ratzel
D) H. J. Mackinder
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
For cotton cultivation which among the following soils is considered most suitable?
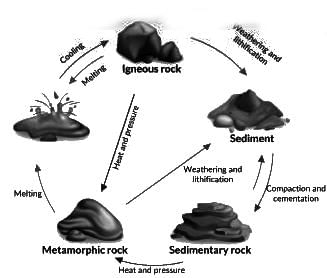
Consider the following statements regarding types of rocks:
1. In general, metallic minerals are found in igneous and metamorphic rock.
2. Igneous and metamorphic rock forms large plateaus.
3. Coal and Petroleum are found in the sedimentary strata.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
Identify the theories/hypotheses that have been put forward to explain the causes of mountain building.
(A) Nebular Hypothesis
(B) Progressive Wave Theory
(C) Contraction Hypothesis
(D) Plate Tectonics Theory
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:Direction: The following item consists of two statements, statement 1 and statement 2. Examine these two statements carefully and select the correct answer from the code given below.
Statement 1:
The salinity of oceans is relatively higher near the equator than in other regions.
Statement 2:
The Equator region has heavy rainfall, high relative humidity and calm air.
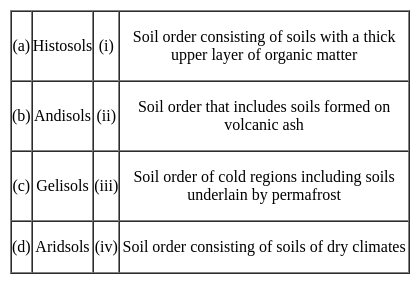
Match the following soil orders with their descriptions:
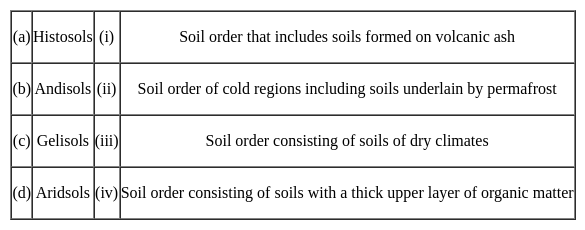
Choose the correct option from those given below:
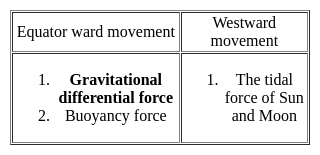
Which of the following statements are correct about the continental drift theory?
1. Wegner aims to explain the relation between past climatic change and the displacement of the continents
2. The supercontinent Pangea breakdown into Laurasia and Gondwanaland.
3. Differential gravitational forces are responsible for the displacement
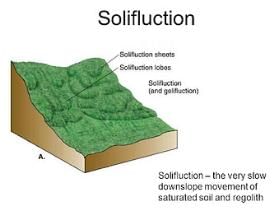
Solifluction is a geomorphic process involving a special type of soil flow that is noticed in
_______ are lines drawn on a map to locate, in the plan view, points of equal ground elevation.
The amount of information to be represented on the map depends on
Periodic change towards unusual colder side is called
…………….. type of rainfall is also called 4’O clock rainfall