UGC NET Paper 2 Education Mock Test - 3 - UGC NET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - UGC NET Paper 2 Education Mock Test - 3
In the Indian social system as it obtains today, the goal of equality and excellence will not be viewed as two opposite poles in terms of whose philosophy?
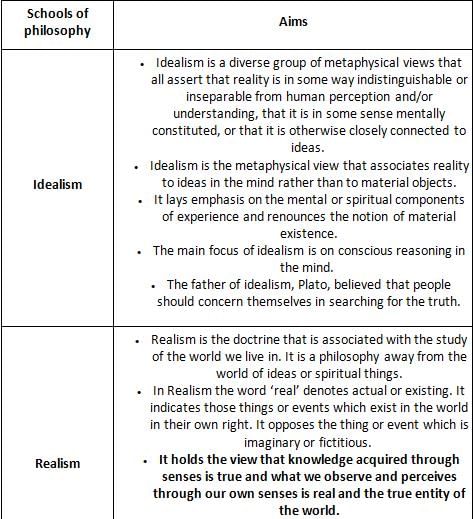
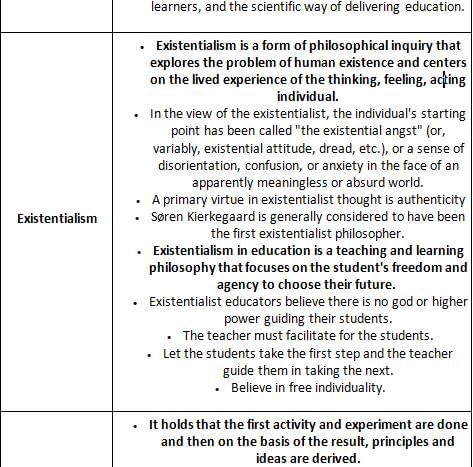
Which school of Western Philosophy endorses the following metaphysical assertion?
"Since the universe exists independent of us and is governed by laws over which we have little control, it is necessary to know certain definite things about this universe in order to adopt to it"
__________ can be viewed as an arrangement of materials prepared in advance and intended for instruction.
Consider the following statements:
I. NPE 1968 was based on the recommendations of Education Commission.
II. It required a “radical restructuring” and equalizing educational opportunities in order to achieve national integration.
Which of the following is/are instrument(s) of survey research?
I. Observation
II. Interview
III. Questionnaire
A procedure intended to establish the quality, performance or reliability of something is known as
What is the importance of having developed senses?
According to Radhakrishnan Commission, the aim of Higher Education is:
Student's needs and interests are important in
The most important element in the Jain theory of Pramanas is
Mark out the reason that made Jawaharlal a great leader.
The concept of the looking-glass self may be summarised as follows
The quality of test that measures ''what it claims to measure'' is?
A test very popular with class room teacher is?
Observational learning is also called
I. Vicarious learning
II. Social learning
III. Modelling
Match List - I with List - II
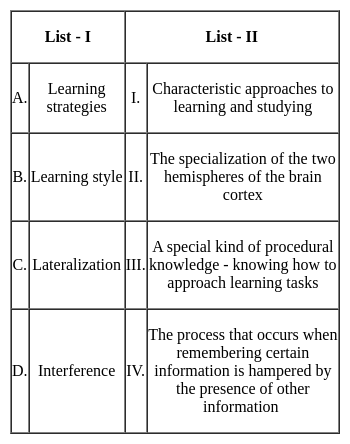
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
The child who tends to reverse letters and numbers in the process of learning, is said to be affected by
According to the passage, what is a seemingly contradictory situation?
Which among the following is an element of the concept development process?
I. Experience
II. Socialisation
III. Abstraction
Assertion (A): A teacher should not cater to individual differences in the class.
Reason (R): The purpose of progressive education is to ensure that all children are instructed in a uniform manner and assessed by standard methods.
Choose the correct option.
The most important characteristic of a society is
If a child is a back bencher and unable to watch the blackboard clearly. As a result he stands, sees and sits repeatedly. What inference will you draw regarding the case?
The current view of childhood assumes that.
Who advanced the concept of ‘creative self’ as the most essential aspect of one’s personality?
Which of the following is directly related to quality enhancement of teacher education programme?