Test: Free Body Diagram- 2 - Grade 12 MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Free Body Diagram- 2
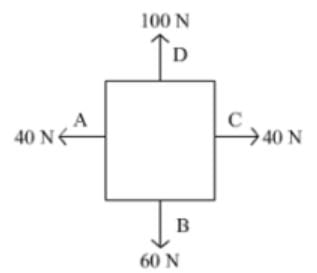
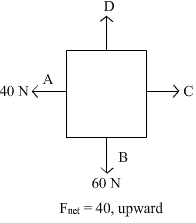
Free body diagram of a situation is shown below. The net force is known, however, the magnitude of few of the forces is not known. The magnitude of the unknown forces C and D will be:
If a block moving up at an inclined plane with θ =30° with a velocity 5 m/s , stops after 0.5 sec , then coefficient of friction is:
A person is sliding an iron box across the floor. Its free body diagram will be
Free body diagram of a box pushed with constant velocity along a rough horizontal surface is
A lift of mass 1000kg , which is moving with an acceleration of 1 m/s2 in upward direction has tension developed in its string equal to: (take g=9.8m/s2)
25 N force is required to raise 75 kg mass from a pulley. If rope is pulled 12 m , then the load is lifted to 3 m , the efficiency of pulley system will be:
An ice cart of mass 60 kg rests on a horizontal snow patch with coefficient of static friction 1/3 . Assuming that there is no vertical acceleration , find the magnitude of maximum horizontal force required to move the ice cart.
A mass of 100 kg is resting on a rough inclined plane of 60o. If the coefficient of friction is 0.5, then the least force acting parallel to the plane to keep the mass in equilibrium is
Three blocks connected together lie on a horizontal frictionless table and pulled to the right with a force of F = 100 N. If m1 = 10 kg, m2 = 20 kg, m3 = 30kg. Then the tension T1 and T2 will be
Block A has mass 10 kg and block B has mass 5 kg. They are connected by an inextensible rope which passes over the mass less and frictionless pulley. Select the correct free body diagrams for two blocks from the given options.