Test: Classification of Polymers (Old NCERT) - JEE MCQ
Test Description
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Classification of Polymers (Old NCERT)
Test: Classification of Polymers (Old NCERT) for JEE 2025 is part of JEE preparation. The Test: Classification of Polymers (Old NCERT) questions and answers have been prepared
according to the JEE exam syllabus.The Test: Classification of Polymers (Old NCERT) MCQs are made for JEE 2025 Exam.
Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Test: Classification of Polymers (Old NCERT) below.
Solutions of Test: Classification of Polymers (Old NCERT) questions in English are available as part of our course for JEE & Test: Classification of Polymers (Old NCERT) solutions in
Hindi for JEE course.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Test: Classification of Polymers (Old NCERT) | 10 questions in 15 minutes | Mock test for JEE preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study for JEE Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Test: Classification of Polymers (Old NCERT) - Question 1
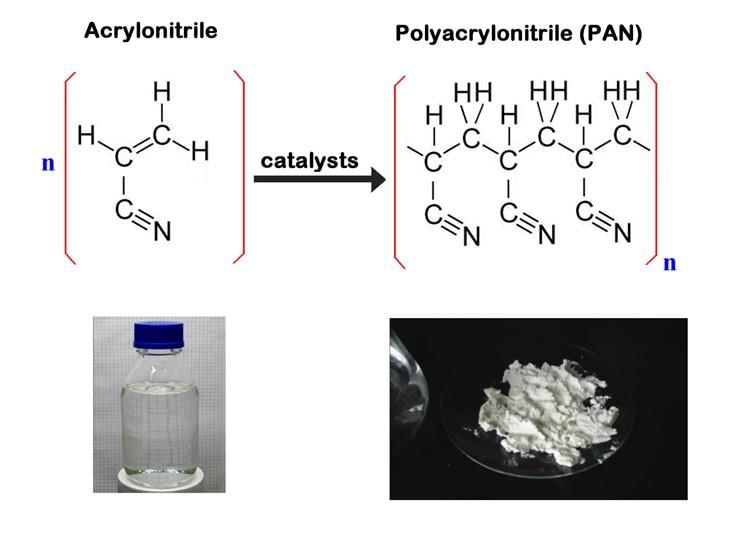
Which one of the following is not a condensation polymer?
Detailed Solution for Test: Classification of Polymers (Old NCERT) - Question 1
Test: Classification of Polymers (Old NCERT) - Question 2
The weakest inter-particle forces are present in:
Detailed Solution for Test: Classification of Polymers (Old NCERT) - Question 2
Test: Classification of Polymers (Old NCERT) - Question 3
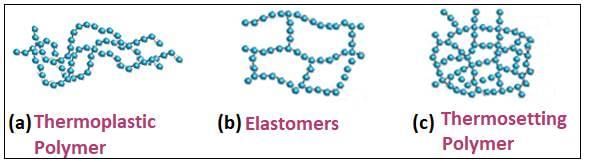
Polymers that are found in nature are called:
Detailed Solution for Test: Classification of Polymers (Old NCERT) - Question 3
Test: Classification of Polymers (Old NCERT) - Question 4
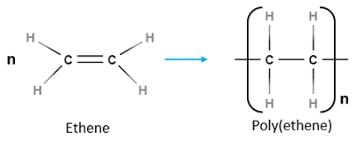
Which polymerisation occurs among the molecules containing double bonds?
Detailed Solution for Test: Classification of Polymers (Old NCERT) - Question 4
Detailed Solution for Test: Classification of Polymers (Old NCERT) - Question 5
Test: Classification of Polymers (Old NCERT) - Question 6
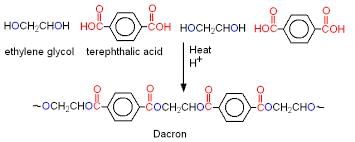
A condensation polymer among the following is:
Detailed Solution for Test: Classification of Polymers (Old NCERT) - Question 6
Detailed Solution for Test: Classification of Polymers (Old NCERT) - Question 7
Detailed Solution for Test: Classification of Polymers (Old NCERT) - Question 8
Test: Classification of Polymers (Old NCERT) - Question 9
The polymers which are prepared in the laboratories are called:
Detailed Solution for Test: Classification of Polymers (Old NCERT) - Question 9
Test: Classification of Polymers (Old NCERT) - Question 10
Which of the following is true for the resultant polymer product formed, when molecules of pthalic acid react with molecules of glycerol?
Detailed Solution for Test: Classification of Polymers (Old NCERT) - Question 10
Information about Test: Classification of Polymers (Old NCERT) Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Test: Classification of Polymers (Old NCERT) solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Test: Classification of Polymers (Old NCERT), EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice
Download as PDF