Test: Energy & Power - JEE MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Energy & Power
How should the force applied on a body be varied with velocity to keep the power of force constant?
An engine generates a power of 10 kW. In how much time will it raise a mass of 200 kg through a height of 40m.
A person 'A' pushes a body of 5 kg placed on a rough surface of co-efficient of friction 0.3 by a distance of 4 m in 15 seconds. Another person 'B' pushes the body of 7 kg on same surface by a distance of 3 m in the same time. Who has more energy and power?
A body moves under a force such that momentum of the body at any instant 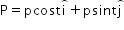 . What is the rate of work done by the force?
. What is the rate of work done by the force?
A man A of mass 80 kg runs up a staircase in 12 seconds. Another man of mass 60 kg runs up the same staircase in 11 seconds. The ratio of powers of A and B is :
If momentum of an object is doubled, how does its kinetic energy change?
An electric motor creates a tension of 4500 N in a hoisting cable and reels it in at the rate of 2 m/s. What is the power of the electric motor?
From a waterfall, water is falling at the rate of 100 kg/s on the blades of a turbine. If the height of fall is 100 m, the power delivered to the turbine is
Calculate the power developed when the force of 10 N is exerted on a body moving with velocity of 3.65 m/s.
A body is moved along a straight line path by a machine delivering constant power. The distance moved by the body in time t is proportional to:




















