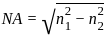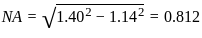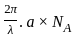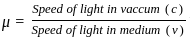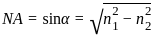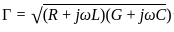ST 15: Optical Fiber Communication - Judiciary Exams MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - ST 15: Optical Fiber Communication
The refractive indices of core and cladding of an optical fiber are 1.40 and 1.14 respectively. What is the value of numerical aperture?
What is the value of maximum number of modes that requires for the successful propagation of light in the fibre?
In a graded index fiber, total reflected light takes a -
Approximately what is the frequency limit of an optical fiber?
In which of the following are the optical fibers commonly used?
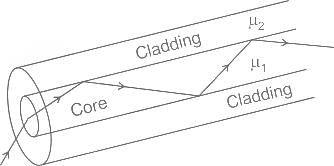
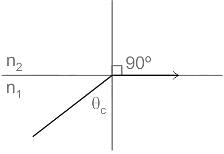
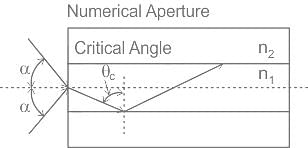
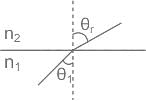
The critical angle θc in an optical fiber is given by ______. Where n1 is refractive index of medium 1 and n2 is the refractive index of medium 2.
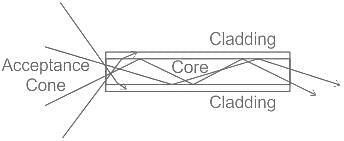
_______ is used to describe the light gathering or light collecting ability of an optical fiber
Which of the following is used as a receiver for fiber optic communication?
Attenuation per unit length in a coaxial cable with frequency_____.
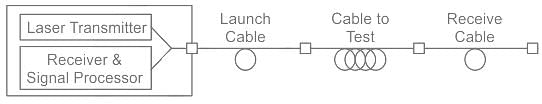
Optical Time domain Reflectometer is used to measure:
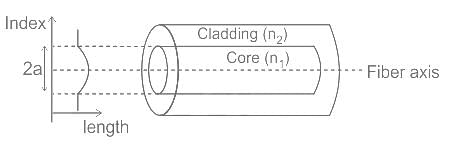
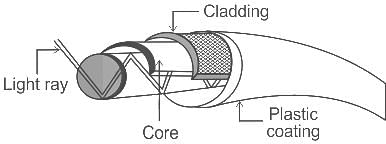
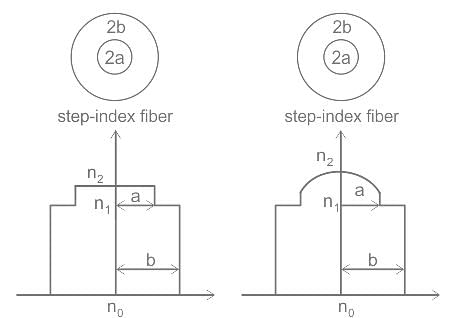
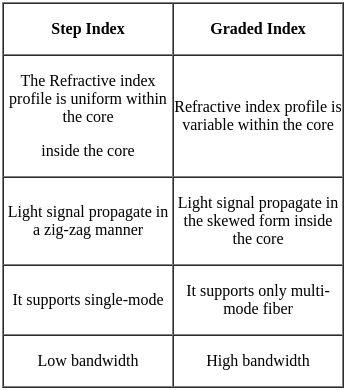
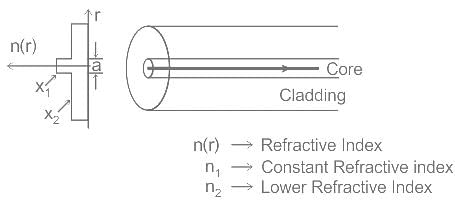
The refractive index of the core is uniform throughout and undergoes an abrupt change at the cladding boundary which is known as ______.
In graded index multimode optical fiber, the refractive index of the core is
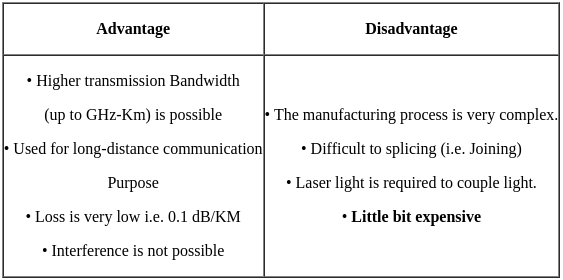
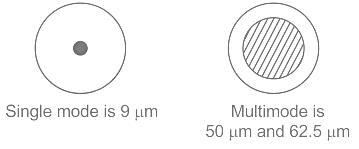
Which fiber is preferred for long distance communication?
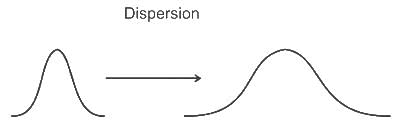
The phenomenon of pulse spreading in optical fibre is known as:
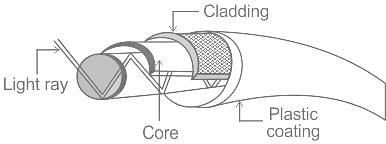
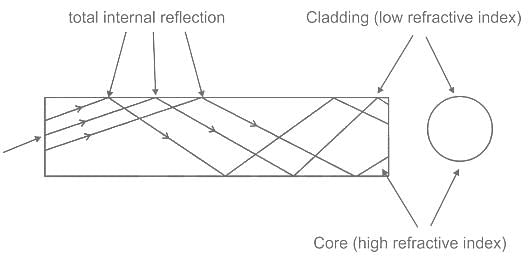
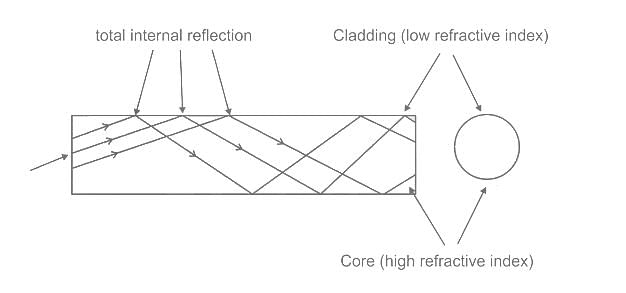
Which of the following is the principle of operation of fibre-optic cable?
In the structure of the fiber optic cable, the refractive index of the core is always ______ the refractive index of the cladding.
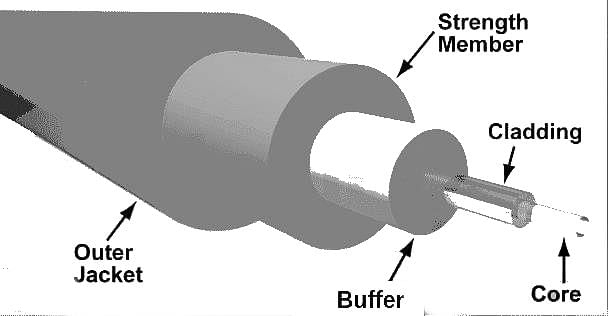
Which of the following is the outermost layer of a fibre optic cable?