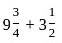Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 1 - Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT/TGT MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 1
Recently, who amongst the following has won the Best Actor Award for the film 'Joram' at the Durban International Film Festival 2023?
What is the primary purpose of the ADITYA-L1 mission?
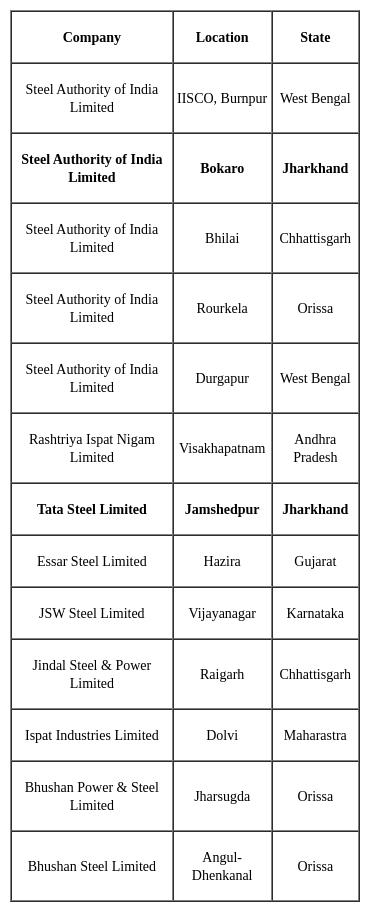
Bokaro is the famous for steel plant which is the biggest in Asia and is built from the help of:
In the times of Mughals the region of Jharkhand was known as _______.
Consider the following statements regarding the Money bill:
1. It is governed by Article 110 of the Constitution of India
2. It cannot be amended or rejected by the Rajya Sabha.
3. President can either accept or reject a money bill but cannot return it for reconsideration.
4. Provision for joint sitting of both the houses is mentioned in constitution to resolve them in case of deadlock.
Which of the statements given above is/are not correct?
Select the correct alternative to indicate the arrangement of the following words in a logical and meaningful order.
1. Quadrilateral
2. Octagon
3. Triangle
4. Decagon
5. HeptagonWhich of the following helps in the blood clotting?
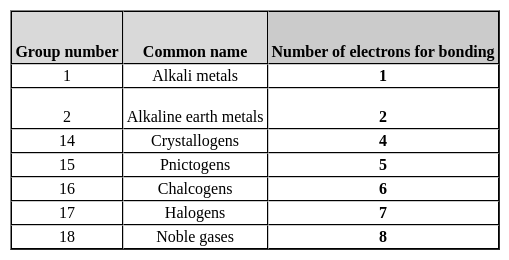
Alkali metals are assigned which group in the Modern Periodic Table?



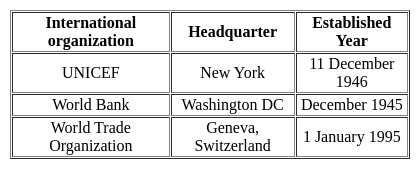
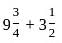 ?
?