MH SET Paper 2 Mock Test - 9 (Geography) - MAHA TET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - MH SET Paper 2 Mock Test - 9 (Geography)
Consider the following:
1. Proximity of the jute-producing areas
2. Inexpensive water transport
3. Availability of economical labor
4. Abundant water for processing raw jute
How many of the above are responsible factors for the location of the Jute industry in the Hugli basin?
How many of the statements given above are correct?
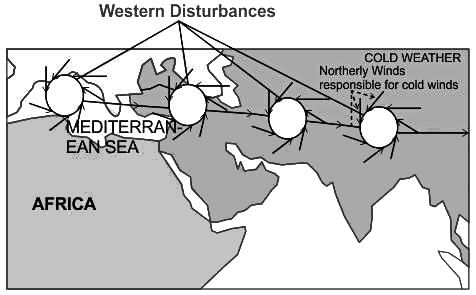
During the cold weather season, in the northern plains, there will be an inflow of cyclonic disturbances from the ______ directions.
Which of the following is/are example(s) of the assertion that cultural differences existing in the world is the outcome of human interaction with the environment?
(A) People of Amazon basin live in houses with a steeply slanting roof.
(B) People of Amazon practice 'slash and burn agriculture'.
(C) People in Bihar and Assam make handicrafts from silk.
In manufacturing industries of India, a micro enterprise is an enterprise where investment in plant and machinery does not exceed ____?
(a) The western coast of Mahrashtra is the region most prone to cyclonic storms.
(b) The river Chambal in the North Indian plain is susceptible to frequent flooding.
(c) The north-eastern states lie in the earthquake prone region.
(d) The eastern coast of India has most vulnerability to cyclones.
Match List-I with List-II
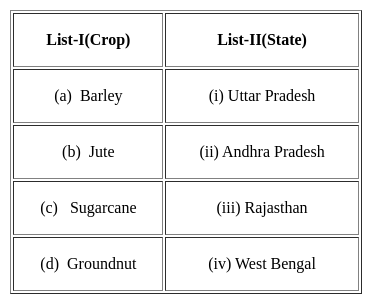
Select the correct answer from the options given below:
Consider the following statements .
(A) Rock is an aggregate of one or more minerals with definite composition of consituent minerals.
(B) Minerals are created by natural process without any human interference.
Choose the correct option.
The temperature-depth profile of the ocean is an interesting topic of study. Which of the following statements is/are incorrect regarding this?
1. About 90 per cent of the total volume of water is found below the thermocline in the deep ocean.
2. The thermocline layer is characterised by a rapid decrease in temperature with increasing depth.
3. The highest temperature of the ocean waters is recorded at the equator.
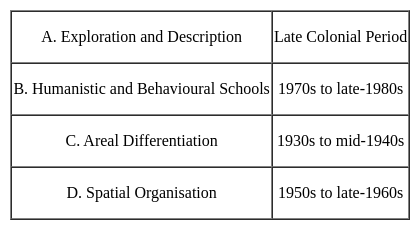
Identify the correct answer from the codes given below.Which of the following is not correctly matched:
Approaches - Periods
When was National environment planning and coordination (NEPC) established?
a. Geostationary satellites, at altitudes of approximately 29,000 km, revolve at speeds which match the rotation of the earth, so they seem stationary.
b. Weather and Communication satellites are commonly found in geosynchronous orbits.
c. Sun-synchronous satellites cover each area of the world at a constant local time of the day with almost no change in azimuth.
d. Geostationary satellites provide conditions for acquiring images in a specific season over successive years.
Which of the above statements are correct?
People move from rural to urban areas mainly for which of the following reasons?
(A) In search of employment
(B) In search of education
(C) In search of better health facilities
(D) In search of better accommodation
With reference to Titanium, consider the following statements:
1. Titanium is present in the Earth’s crust at a level of about 0.6% and is, therefore, the fourth most abundant structural metal after aluminum, iron and magnesium.
2. It is present in most igneous rocks and in sediments derived from them.
3. As of 2021, Russia had the largest reserves of titanium minerals worldwide.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
Assertion (A): The Puranas name the region of Madagascar and Eastern Africa as Shalmali.
Reason (R) : The region of East-Africa is rich in silk-cotton trees.
Select the correct answer from options given below:
Which among the following states leads in Handloom and Handicrafts clusters in India?
Consider the Urban Settlements:
1. Conurbation
2. Megalopolis
3. Million City
4. Town
Which of the following is the correct sequence of the Urban settlements according to their increasing size?
The use of microorganism metabolism to remove pollutants such as oil spills in the water bodies is known as :