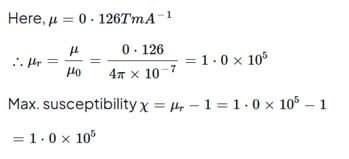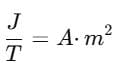Test: Magnetic Properties - JEE MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Magnetic Properties
The magnetic induction left behind in the sample after the magnetizing field has been removed is called
The ferromagnetic materials can be magnetised easily because
What kinds of materials are used for coating magnetic tapes?
A particle of charge q and mass m moves in a circular orbit of radius r with angular speed. The ratio of the magnitude of its magnetic moment to that of its angular momentum depends on
A wire of length L m carrying current i A is bent in the form of a circle. The magnitude of magnetic moment is
If the susceptibility of a metal at saturation is 4500, then what is the permeability of this metal at saturation?
The maximum value of permeability of a metal (77% Ni , 16% Fe , 5% Cu , 2% Cr) is 0.126 T-m/A. What will be the maximum relative permeability and susceptibility?
The units of magnetic pole strength and magnetic dipole moment of a bar magnet are