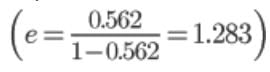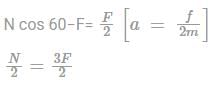ISRO Draughtsman Civil Mock Test - 3 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - ISRO Draughtsman Civil Mock Test - 3
The maximum n permissible shear stress given in BIS 456-1978 is based on
Which type of hall can be generally used for moderate discharge of 40-60 cumes and low fall heights of 1m to 1.5 m?
The resistance of an aggregate to impact is known as
According to the Dickens formula, the flood discharge Q in cumes is given by
In a beam, the diagonal tension is inclined at an angle of –– with horizontal.
Calculate the volume (cubic meter) of earthwork for an embankment of length 30 m and width 4 m. The mean depth of the embankment is 4 m and side slope is 2: 1. Using mid-sectional area method.
Consider the following statements :
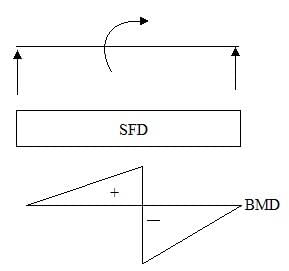
A simply-supported beamish subjected to a couple somewhere in the span. It would produce
1. A rectangular SF diagram
2. parabolic BM diagrams
3. both + ve and - ve BMs are maximum at the point of application of the couple.
Of these statements
Find out the set among the four sets which is like the given set.
Given set is (63, 54, 45)
A sample of saturated clay has a porosity of 0.562. The void ratio of the clay is;
Shrinkage in concrete can be reduced by using-
According to IS code, the flexural strength in (N/mm2) is given as:
Von-Karmon at a definite distance from the wall -
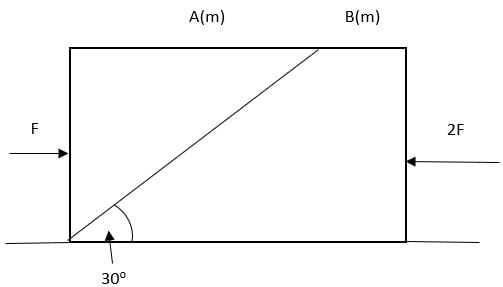
Two blocks A and B, each of mass m, are placed on a smooth horizontal surface. Two horizontal forces F and 2F, are applied on blocks A and B, respectively, as shown in Figure. Block a does not slide on block B. Then the normal reaction acting between the two blocks in (assume no friction between the blocks).
Rapid setting cement contains a relatively higher proportion of
For the flow, through the soils, to be laminar, the Reynolds number shall be-
The detention period for oxidation bonds is usually kept as :
The Muller-Breslau principal for influence line is applicable for-
IS code for standard penetration test in the soil is:
Consider the following statements –
1. The size of a theodolite is defined by the diameter of the graduated circle of the lower plate.
2. The process of establishing intermediate points, on a given straight line whose ends are intervisible, is done with a theodolite is called lining in.
3. Removal of parallax may be achieved by refocusing the eyepiece.
4. An imaginary line passing through the optical center of the eyepiece in the telescope of a surveying instrument is called the line of collimation.
Which of the above statement are correct?
Consider the following statement:
A) Sprinkler method of irrigation has a higher water application efficiency.
B) The duty of drip irrigation is very high due to losses are least in this irrigation system.
Which of the following is/are correct?
The water meter, which is installed on individual house connection, on municipal supply is: