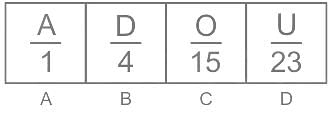
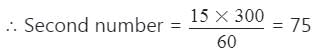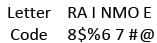HPCL Mechanical Engineer Mock Test - 2 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - HPCL Mechanical Engineer Mock Test - 2
Directions: In the given sentence, an idiom or phrase is missing. Choose the phrase/idiom that can fill the blank both grammatically and contextually.
Do not give much importance to the critics, they are like the _______________ who have not done it themselves in life.
Find out the Synonym of the following word:
STERILE
Two irrational numbers between 2 and 2.5 are :-
If there are n zeros after the decimal point, then the characteristic of that number will be
The decimal expansion 0.080080008000080000080000008….. is a
The HCF of two numbers is 15 and their LCM is 300. If one of the number is 60, the other is :
For a given AP, a(n) = 4, n = 7, d = -4, find the value of a
Which of the following is an example of two dimensions
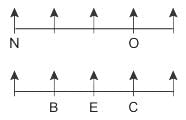
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
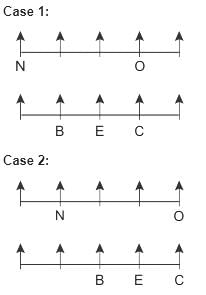
Ten people are sitting in two parallel rows such that people sitting in row 2 are just behind people in row 1. In row 1 - M, N, O, P and Q are sitting and all are facing north. In row 2 - A, B, C, D and E are sitting and all are facing north.
One who sits just behind O is to the immediate right of E. O sits 3rd to the right of N. B is neither at any of the extreme ends nor sits exactly behind O. P sits on a seat which is exactly ahead of A. D doesn’t sit at any of the extreme ends. M is not exactly ahead of E. Number of people sitting between C and E, is the same as the number of people sitting between E and B.
Q. What is the position of D with respect to E?
If '+' means '×', '×' means '–', and '÷' means '+', then which of the following would be the value of 14 ÷ 2 + 8 × 5?
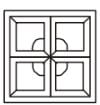
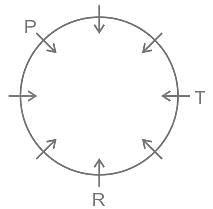
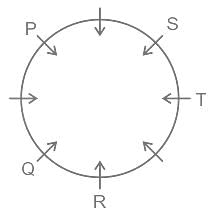
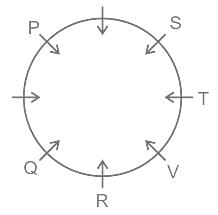
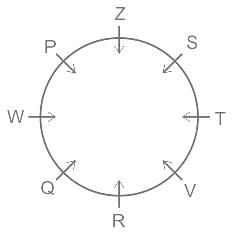
Which answer figure will complete the pattern in the question figure?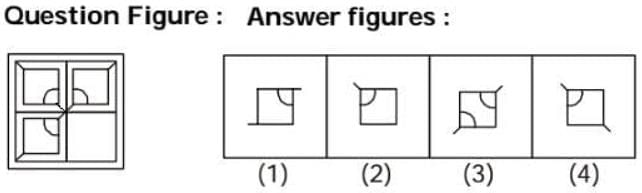
Directions: Study the following question carefully and choose the right answer.
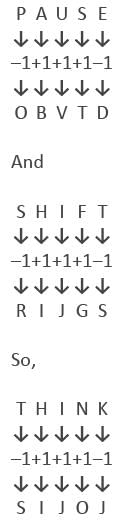
In a certain code PAUSE is written as OBVTD and SHIFT is written as RIJGS. How will THINK be written in the same code?
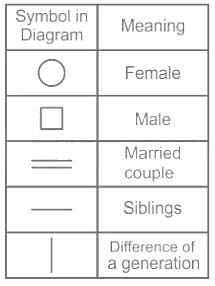
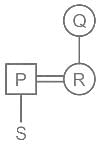
P is father of S. Q is mother of R. R is the mother of S. How is Q is related to S?
Choose the word which is different from the rest.
Direction: Study the following question carefully and choose the right answer.
In a certain code, RAIN is written as 8$%6 and MORE is written as 7#8@. How is REMAIN written in that code?
A short column of external diameter D and internal diameter d carries an eccentric load W.
The greatest eccentricity which the load can be applied without producing tension on the crosssection of the column would be
If the principal stresses on a plane stress problem are s1 = 100 MPa and s2 = 40 MPa, then themagnitude of shear stress (in MPa) will be
The size of an atom is approximately equal to-
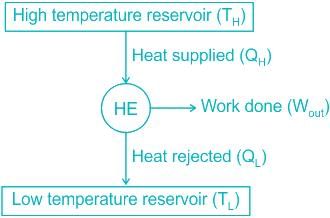
The coefficient of performance of a refrigeration working on a reversed Carnot cycel is 4. Theratio of the highest absolute temperature to the lowest absolute temperature is
What is the maximum possible theoretical efficiency of a heat engine operating with a hot reservoir of gases at 2127°C, when the cooling water available is at 27°C?
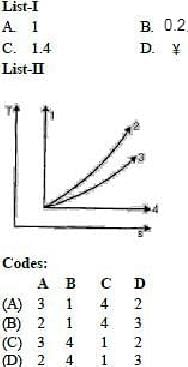
Match List-I (Process index 'n') with List-Ii (Ts traces) and select the correct answer using the
code given below the list
The ratio of the depth of the bucket for a Pelton wheel to the diameter of a jet is of the order of _____.
In oxy-acetylene gas welding, for complete combustion, the volume of oxygen required perunit of acetylene is