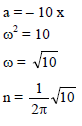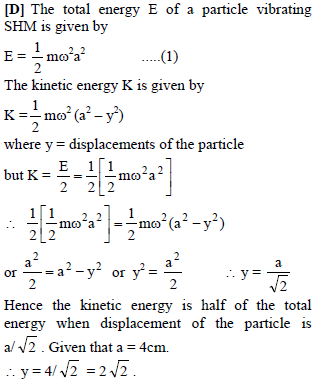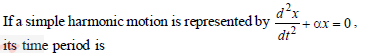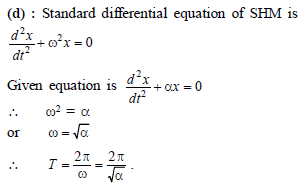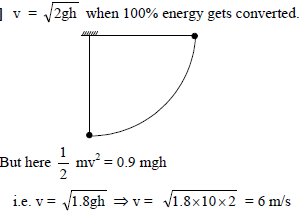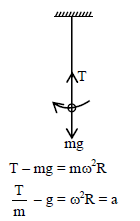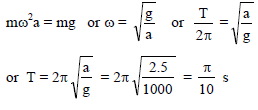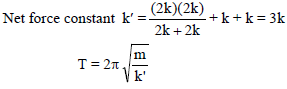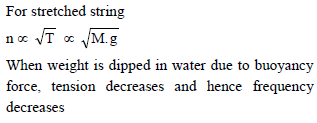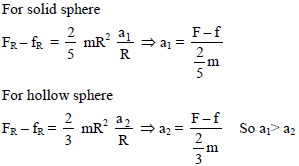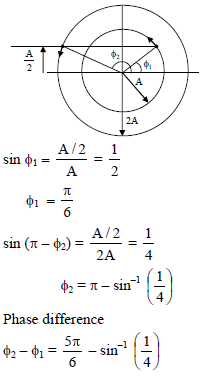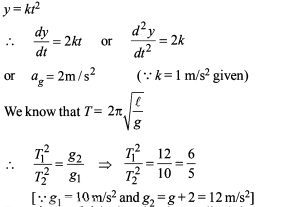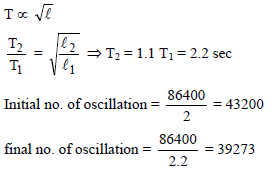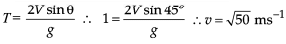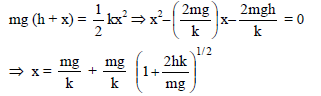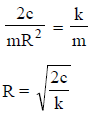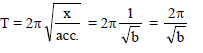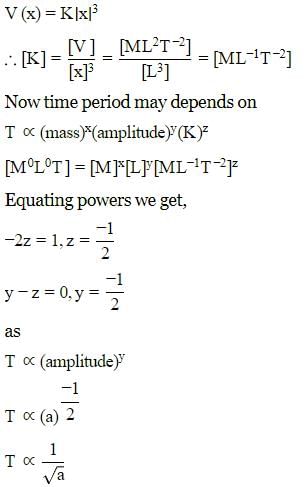Chapter Test: SHM - 2 - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Chapter Test: SHM - 2
The acceleration-displacement (a-x) graph of a particle executing simple motion is shown in figure. The frequency of oscillation is given by -
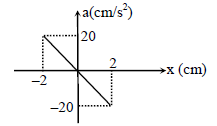
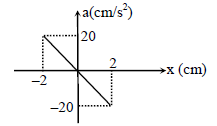
A particle is vibrating in simple harmonic motion with an amplitude of 4 cm. At what displacement from the equilibrium position is its energy half potential and half kinetic ?
A pendulum of length 200 cm is horizontal when its bob of mass 200 gm is released. It has 90% of initial energy when the bob reaches the lower most point. Speed of the bob at this point is -
A simple pendulum with angular frequency ω oscillates simple harmonically. The tension in the string at lowest point is T. The total acceleration of the bob at its lowest position is -
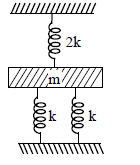
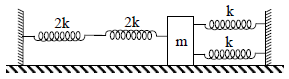
What is the spring constant for the combination of spring shown in fig. ?
A horizontal platform with an object placed on it is executing SHM in the vertical direction. The amplitude of oscillation is 2.5 cm. What must be the least period of these oscillation so that the object is not detached ?
A mass m is attached to four springs of spring constants 2k, 2k, k, k as shown in figure. The mass is capable of oscillating on a frictionless horizontal floor. If it is displaced slightly and released the frequency of resulting SHM would be –
For definite length of wire, if the weight used for applying tension is immersed in water, then frequency will -
Two blocks of masses 10 kg and 2 kg are connected by an ideal spring of spring constant 1000 N/m and the system is placed on a horizontal surface as shown.
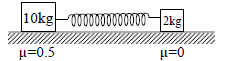
The coefficient of friction between 10 kg block and surface is 0.5 but friction is assumed to be absent between 2 kg and surface. Initially blocks are at rest and spring is unstretched then 2 kg block is displaced by 1 cm to elongate the spring then released. Then the graph representing magnitude of frictional force on 10 kg and time t. (time t is measured from that instant when 2kg is released to move)
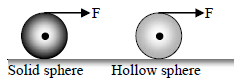
A constant horizontal force F is applied on the top of a solid sphere and a hollow sphere of same mass and radius both kept on a sufficiently rough surface. Let a1 and a2 be their linear accelerations, then :
Two particles are in SHM with same angular frequency and amplitudes A and 2A respectively along same straight line with same mean position. They cross each other at position A/2 distance from mean position in opposite direction. The phase difference between them is
If the length of second pendulum is increased by 21%. How many oscillations it will lose per day
A solid ball of mass m is allowed to fall from a height h to a pan suspended with a spring of spring constant k. Assume the ball does not rebound and pan is massless, then amplitude of the oscillation is -
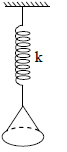
A solid disk of radius R is suspended from a spring of linear spring constant k and torsional constant c, as shown in figure. In terms of k and c, what value of R will give the same period for the vertical and torsional oscillations of this system?
The periodic time of S.H.M. of amplitude 2 cm is 5 sec. If the amplitude is made 4 cm, its periodic time will be -
The motion of a particle is expressed by the equation acc. a = – bx where x is displacement from equilibrium position and b is constant. What is the periodic time ?
A particle of mass m is executing oscillation about the origin on X-axis. Its potential energy is V(x)=K∣x∣3. Where K is a positive constant. If the amplitude of oscillation is a, then its time period T is proportional to.
If the reference particle P moves in uniform circular motion, its projection along a diameter of the circle executes
If the sign in equation F = -kx is changed what would happen to the motion of the oscillating body?
What is the maximum Kinetic energy and minimum potential energy of a harmonic oscillator with amplitude 0.03m, force constant 4×105 N/m and total mechanical energy of 230 J.
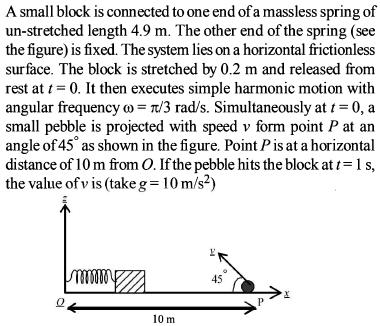
A particle starts S.H.M. from the mean position. Its amplitude is A and time period is T. At the time when its speed is half of the maximum speed, its displacement y is