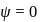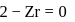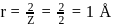Test: Electronic configuration, Quantum Mechanical Model - JEE MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Electronic configuration, Quantum Mechanical Model
Which of the following is not permissible arrangement of electrons in an atom?
The orbital diagram in which the Aufbau principle is violated is:
What are the numbers of angular nodes and radial nodes for 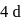 -orbitals respectively?
-orbitals respectively?
The electrons identified by quantum numbers 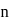 and
and 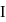 :
:
a) 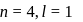
b) 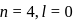
c) 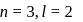
d) 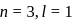
Can be placed in order of increasing energy
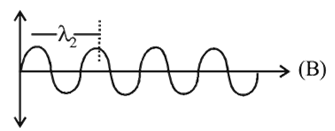
What will be the difference between electromagnetic radiation shown in A and B respectively ?
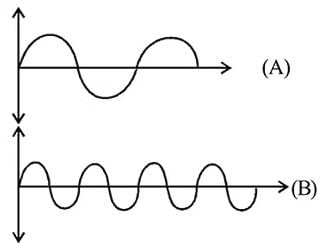
(i) Velocity
(ii) Wavelength
(iii) Frequency
(iv) Energy
Which of the following radial distribution graphs correspond to 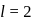 for the
for the 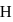 atom ?
atom ?
Which combinations of quantum numbers, n,l, m and s for the electron in an atom does not provide a permissible solution of the wave equation?
Which of the following should be the number of electrons present in 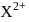 on the basis of electronic configuration, if the ion
on the basis of electronic configuration, if the ion 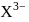 has 14 protons?
has 14 protons?
Which one of the following set of quantum numbers is not possible for 4p electron?
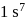 it would have energy lower than that of the normal ground state configuration
it would have energy lower than that of the normal ground state configuration 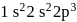 because the electrons would be closer to the nucleus. Yet
because the electrons would be closer to the nucleus. Yet 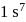 is not observed. It violates
is not observed. It violates
The correct order of increasing energy of atomic orbitals is
The ratio of magnetic moments of Fe(III) and Co(II)s
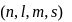 ?
?
Which of the following symbols correctly represents an orbitals in an atom?
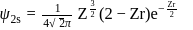
The radius for nodal surface for
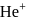 ion in
ion in 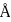 .
.
When 4 f subshell is completely filled with electrons, the next electron will enter into a subshell for which, (n+L) value is equal to


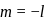 to
to 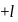 , through zero thus for
, through zero thus for 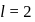 values of
values of 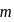 will be
will be 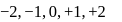
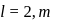 cannot have the value
cannot have the value 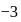
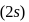 should be fully filled before the filling of orbital of higher energy starts.
should be fully filled before the filling of orbital of higher energy starts.
 It is also known as a nodal plane.
It is also known as a nodal plane. It is a plane that is passing through the nucleus.
It is a plane that is passing through the nucleus.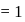
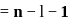
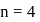
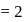
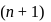 , the greater is the energy of orbitals.
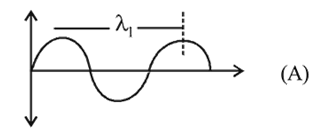
, the greater is the energy of orbitals. waves shown in figure
waves shown in figure  has higher wavelength in comparison to
has higher wavelength in comparison to  waves shown in figure
waves shown in figure 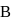 .
.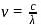
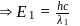
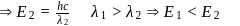
 represent
represent  orbital for which
orbital for which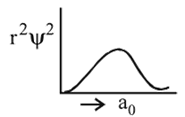
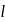 and
and 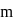 depend upon the value of
depend upon the value of 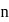
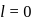 to
to 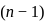
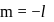 to
to 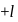 through zero
through zero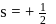 and
and 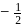
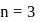
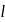 may be 0,1 or
may be 0,1 or 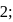 but not 3
but not 3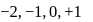 or
or 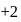
 may
may 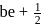 or
or 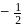
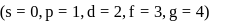
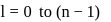 , n should be atleast 5.
, n should be atleast 5.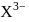 has 14 protons, i.e.,
has 14 protons, i.e.,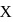 also has 14 protons and therefore 14 electrons.
also has 14 protons and therefore 14 electrons.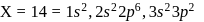
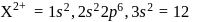 electrons
electrons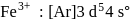
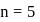
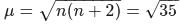
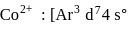
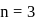
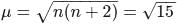
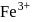 and
and 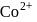 is:
is: 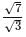
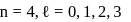
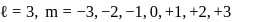
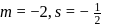
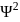 cannot be imaginary.
cannot be imaginary. 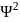 is positive for a real wave function and
is positive for a real wave function and 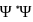 (where
(where 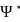 is the complex conjugate of
is the complex conjugate of 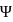 ) is positive.
) is positive.