Test: Law of Mass Action, Equilibrium Constants (Kc and Kp) - JEE MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Law of Mass Action, Equilibrium Constants (Kc and Kp)
At T( K), the equilibrium constant of H2(g) + I2(g) ⇌ 2HI(g) is 49. If [H2],[I2] at equilibrium at the same temperature are 2.0 × 10−2M and 8.0 × 10−2M respectively, the [HI] at equilibrium in molL−1 is
For a reversible reaction, if the concentration of the reactants is reduced to half, the equilibrium constant will be.........
Which among the following denotes the correct relationship between 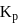 and
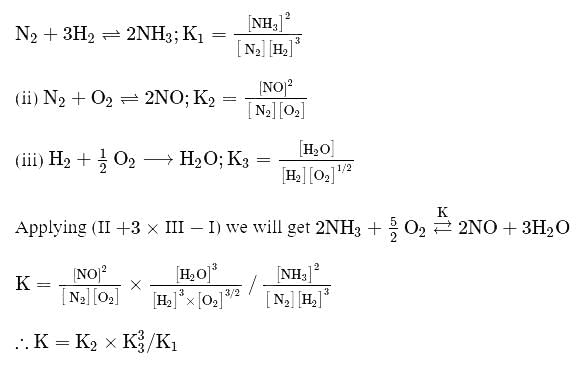
and 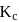 for the reaction
for the reaction 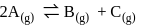
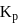 and
and 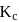 for the reaction
for the reaction 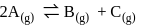
Kc for the reaction N2(g) + O2(g) ⇌ 2NO(g) at 300 K is 4.0 × 10−6. Kp for the above reaction will be (R = 2calmol−1 K−1)
The equilibrium constant of the following are :
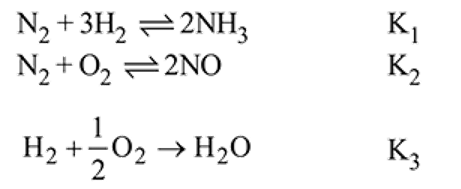
The equilibrium constant 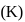 of the reaction :
of the reaction :
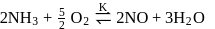 , will be
, will be
The degree of dissociation of PCl5(α) obeying the equilibrium PCl5 ⇌ PCl3 + Cl2 is related to the equilibrium pressure by
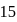 moles of
moles of 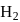 and
and 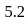 moles of
moles of 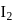 are mixed and allowed to attain equilibrium at
are mixed and allowed to attain equilibrium at 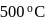 . At equilibrium, the number of moles of
. At equilibrium, the number of moles of 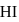 is found to be
is found to be 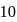 mole. The equilibrium constant for the formation of
mole. The equilibrium constant for the formation of 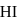 is
is
For the reaction H2(g) + I2( g) ⇌ 2HI(g) at 721 K, the value of equilibrium constant is 50, when equilibrium concentration of both is 5M. Value of Kp under the same conditions will be
For a reversible gaseous reaction 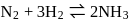 at equilibrium, if some moles of
at equilibrium, if some moles of 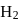 are replaced by same number of moles of
are replaced by same number of moles of 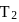 (T is tritium, isotope of
(T is tritium, isotope of  and assume isotopes do not have different chemical properties) without affecting other parameter, then:
and assume isotopes do not have different chemical properties) without affecting other parameter, then:
The ratio 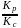 for the reaction
for the reaction  is:
is:
Which of the following is true at chemical equilibrium?
Consider the expression 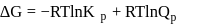 and indicate the correct statement at equilibrium
and indicate the correct statement at equilibrium
If the synthesis of ammonia from Haber's process is carried out with exactly the same starting conditions (of partial pressure and temperature) but using 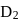 (deuterium) in place of
(deuterium) in place of 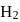 . Then
. Then
In which of the following reactions, the concentration of product is higher than the concentration of reactant at equilibrium? (K = equilibrium constant)
The increase of pressure on ice 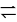 water system at constant temperature will lead to
water system at constant temperature will lead to


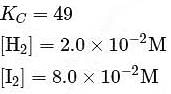
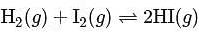
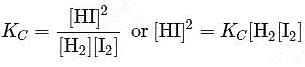
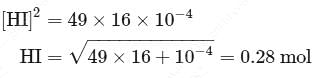
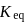 is independent of initial concentrations of reactants and products. So, options (a), (b) and (c) are not correct, i.e. so, for a reversible reaction, if the concentration of the reactants is reduced to half, the equilibrium constant will be remains same.
is independent of initial concentrations of reactants and products. So, options (a), (b) and (c) are not correct, i.e. so, for a reversible reaction, if the concentration of the reactants is reduced to half, the equilibrium constant will be remains same.
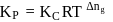
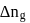 is the difference of the gaseous number of moles of reactant side and product side
is the difference of the gaseous number of moles of reactant side and product side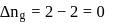
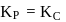
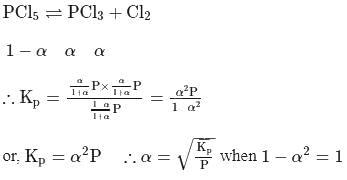


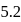
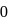
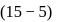
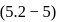

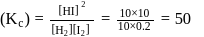
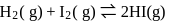
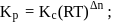
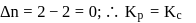
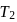 has similar chemical properties as
has similar chemical properties as 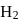 so upon mixing,
so upon mixing, 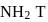 and
and  are formed.
are formed.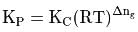
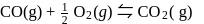

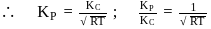
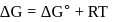
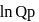
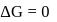
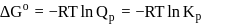
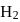 or
or 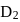 reach equilibrium with the same composition, except that
reach equilibrium with the same composition, except that 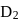 and
and 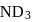 are present instead of
are present instead of 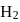 and
and 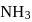 .
.
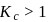 , then [Product] > [Reactant]
, then [Product] > [Reactant]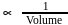 So equilibrium, will shift forward.
So equilibrium, will shift forward.
















