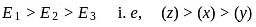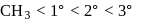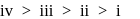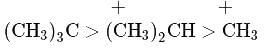Test: Reaction Intermediates, Attacking reagents - JEE MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Reaction Intermediates, Attacking reagents
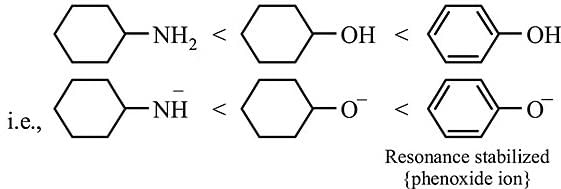
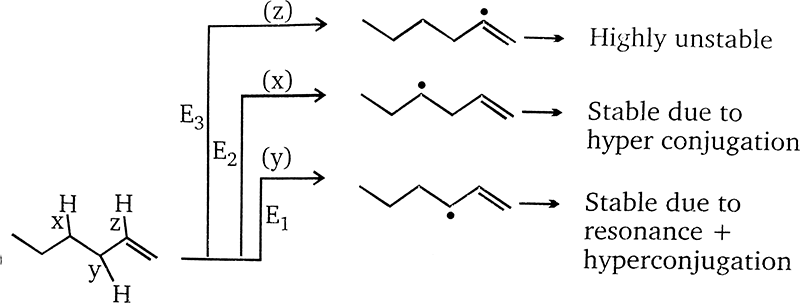
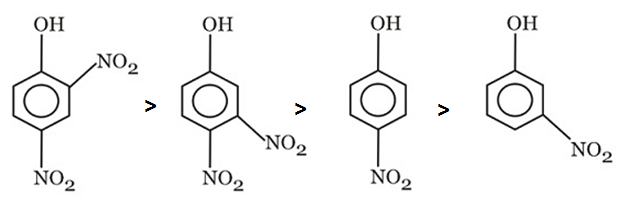
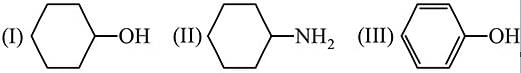
Arrange in the order of increasing acidity.

Heterolysis of carbon-chlorine bond produces
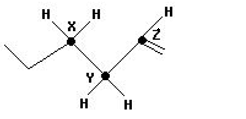
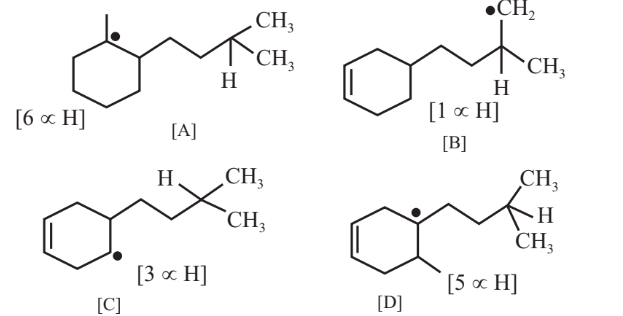
Arrange the C-H bods ′x′,′y′ and ′z′ in decreasing order of their bond dissociation energies homolysis

Arrange the C-H bods ′x′,′y′ and ′z′ in decreasing order of their bond dissociation energies homolysis
Which of the following represents the correct order of stability of the given carbocations?
Arrange the following free radicals in the correct order of their stability
(i) 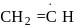
(ii) 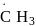
(iii) 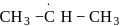
(iv) 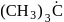
In the following compounds
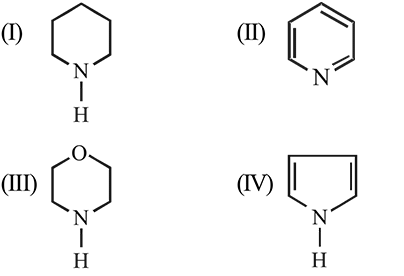
the order of basicity is :
Which of the following statements is not correct?
Which is the most stable carbocation?
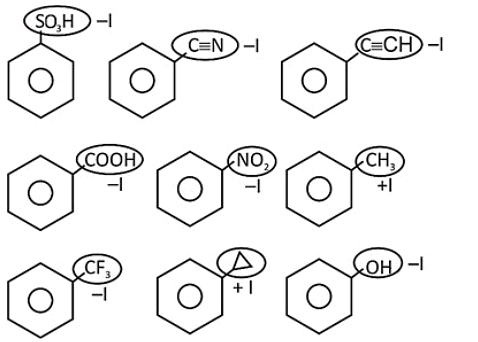
X = number of compounds having -I group directly attached to benzene.
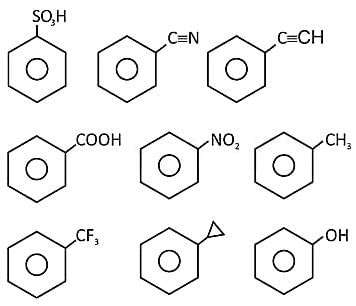
Find the value of 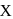 ?
?
Correct order of reactivity of following compounds towards Grignard reagent?
Which of the following alkenes is the most stable?
Which one amongst the following carbocations is most stable?
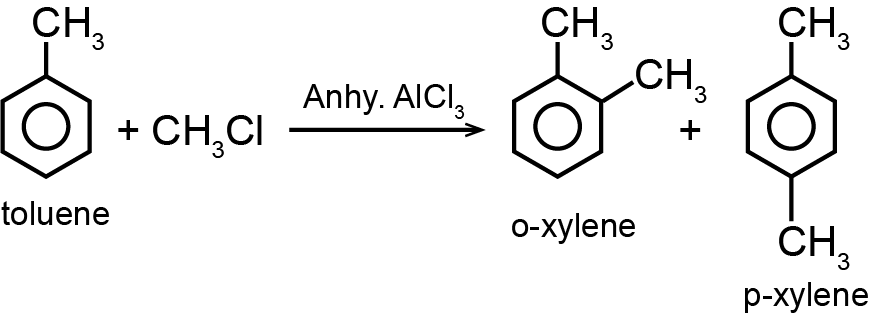
Friedel-Craft's reaction using MeCl and anhydrous AlCl  will take place most efficiently with
will take place most efficiently with
Which of the following carbocations is expected to be most stable?
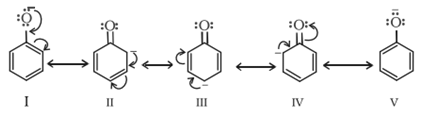
Which of the following species is expected to yield maximum percentage of meta substitution product?
Arrange the carbanions, (CH3)3C−,Cl3C−,(CH3)2CH−,C6H5CH2−, in order of their decreasing stability.
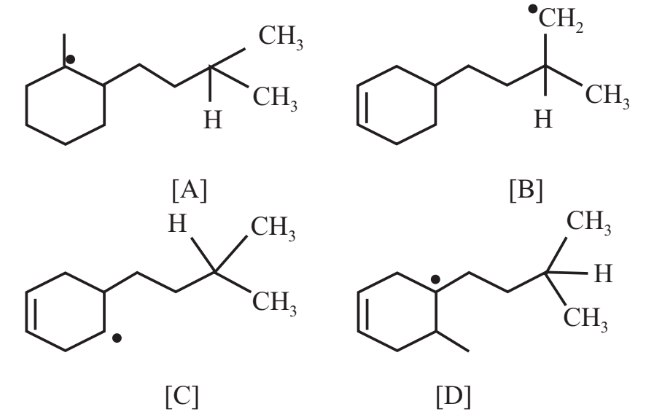
For the following radicals, the correct order of their stability is
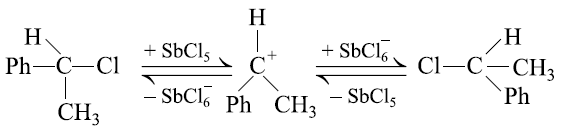
A solution of (−)−1− chloro-1-phenylethane in toluene racemises slowly in the presence of a small amount of SbCl5 due to the formation of
Among the following, the strongest base is
Most acidic hydrogen containing compound among the following is