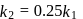Test: Rate law and rate constant - JEE MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Rate law and rate constant
In a certain polluted atmosphere containing O3 at a steady concentration of 2.0 x 10-6 M, the hourly production of O3 by all sources was estimated as 7.2 x 10-15 M. If the only mechanism for destruction of O3 in the second-order reaction is
2O3 → 3O2
then rate constant for destruction reaction, defined by the rate law for - Δ[O3]/Δf is x * 10-7 M-1 s-1 . What is the value of x?
Only One Option Correct Type
This section contains 2 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct
For a reversible reaction, net rate is
(dx/dt) = k1[A]2[B]−1−k2[C]
hence given reaction is
The rate constants for a reaction at 400 K and 500 K are 2.60 x 10-5 s-1 and 2.60 x 10-3 s-1,respectively. The activation energy of the reaction in kJmol-1 is ______
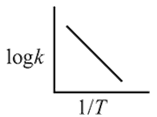
A reaction rate constant is given by k=1.2×1014 e−25000/RTsec−1. It means
The time required for 10% completion of a first order reaction at 298K is equal to that required for its 25% completion at 308K If the preexponential factor for the reaction is 3.56 x 109 s-1, the activation energy at 318K is:
In a reaction A → Products, when start is made from 8.0 × 10−2 M of A, half-life is found to be 120 minute. For the initial concentration 4.0 × 10−2 M, the half-life of the reaction becomes 240 minute. The order of the reaction is:
For the reaction A + B⟶ products, it is observed that:
(1) On doubling the initial concentration of A only, the rate of reaction is also doubled and
(2) On doubling the initial concentrations of both A and B, there is a change by a factor of 8 in the rate of the reaction. The rate of this reaction is given by:
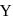 , is zero. It implies that:
, is zero. It implies that:
The rate law for the reaction below is given by the expression k[A][B]
A + B → Product
If the concentration of B is increased from 0.1 to 0.3 mole, keeping the value of A at 0.1 mole, the rate constant will be:
I
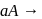 Products,
Products, 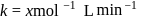
II
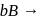 Products,
Products, 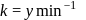
The half-lives of both the reactions are the same, equal to
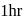 when molar concentration of the reactant is
when molar concentration of the reactant is 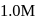 in each case. If these reactions are started at the same time taking
in each case. If these reactions are started at the same time taking 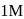 of the reactant in each case, the ratio
of the reactant in each case, the ratio 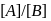 after
after 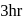 will be :
will be :
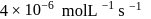 when the concentration of the reactant is
when the concentration of the reactant is 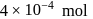
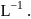 The rate constant of the reaction will be
The rate constant of the reaction will be
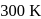 and
and 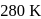 . The rate constants were found to be
. The rate constants were found to be 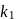 and
and 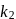 respectively. then
respectively. then




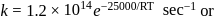
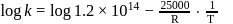
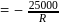
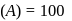
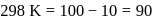
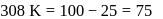
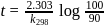 ...(i)
...(i)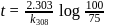 ...(ii)
...(ii)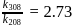
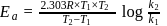
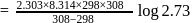
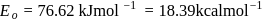
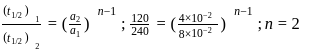
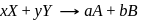
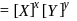
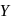 is zero.
is zero. 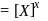
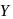 .
.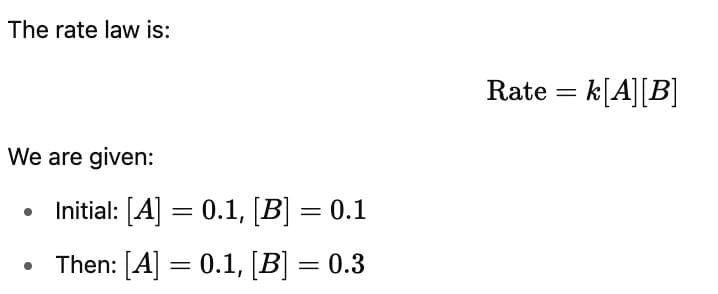
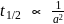
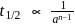
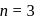 Thus reaction is of
Thus reaction is of 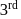 order
order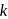 indicate that reaction
indicate that reaction 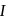 is of second order and reaction
is of second order and reaction 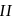 is first order. For
is first order. For 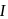 reaction,
reaction, 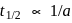 , first
, first 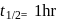 , second
, second 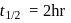
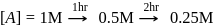
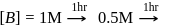
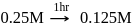
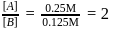
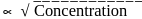
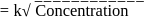

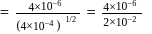
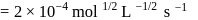
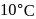 rise in temperature. For
rise in temperature. For 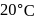 rise, the rate constant will be 4 times
rise, the rate constant will be 4 times 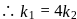 or
or