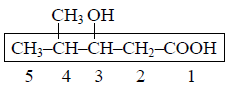General Organic Chemistry (GOC) - 1 - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - General Organic Chemistry (GOC) - 1
The IUPAC name of the compound
CH₃CH=CHC≡CH is:
CH₃CH=CHC≡CH is:
The total number of π-bond electrons in the following structure is:
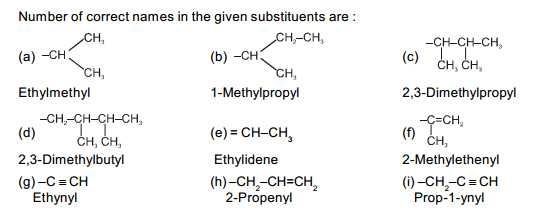
The correct decreasing order of priority for the functional groups of organic compounds in the IUPAC system of nomenclature is
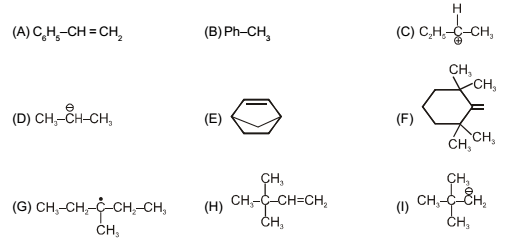
In which of the following compounds is there more than one kind of hybridization (sp, sp², sp³) for carbon?
The IUPAC name of the compound
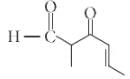 is ______.
is ______.
Which of the following is saturated homocyclic compound.
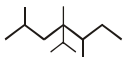
In the structure of 4-Isopropyl-2,4,5-trimethylheptane, number of 10, 20 & 30 H’s are respectively.
IUPAC nomenclature of the given organic compound will be : (CH3)2C(CH2CH3)CH2CH(Cl)CH3 :
In allene (C3H4), the type(s) of hybridisation of the carbon atoms is (are) :
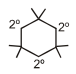
A hydrocarbon (R) has six membered ring in which there is no unsaturation. Two alkyl groups are attached to the ring adjacent to each other. One group has 3 carbon atoms with branching at 1st carbon atom of chain and another has 4 carbon atoms. The larger alkyl group has main chain of three carbon atoms of which second carbon is substituted. Number of 2° carbons in R are :
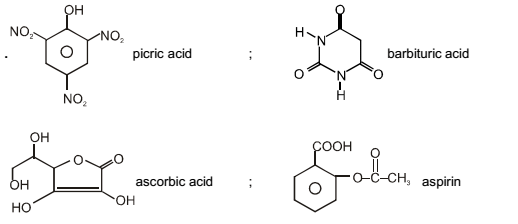
The carboxyl functional group (– COOH) is present in :
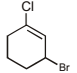
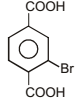
The correct IUPAC name for the compound
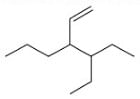 is ______.
is ______.
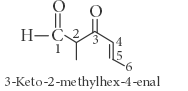
The correct IUPAC name for the compound
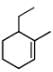 is ______.
is ______.
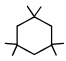
In above compound total number of 2º hydrogen atoms are :
The IUPAC name of the following compound is -
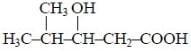
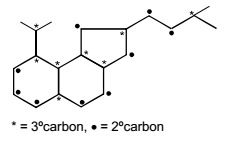
Number of 3º and 2º carbon atoms in the following compound are.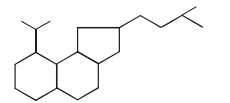
Which of the following statements is not correct?
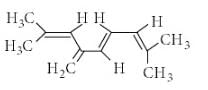
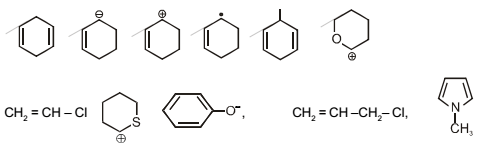
How many of the following species can show resonance.
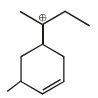
Observe the following compound and write the number of hydrogen atom involved in hyperconjugation ?
Which of the following groups cannot participate in resonance with benzene :
Among the following four compounds:
(i) Phenol
(ii) Methyl phenol
(iii) Meta-nitrophenol
(iv) Para-nitrophenol
The acidity order is:
In how many of the following compounds Hyperconjugation effect is observed -










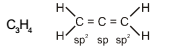

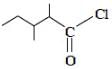 is ______.
is ______.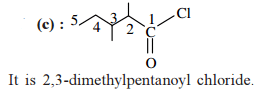
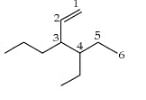
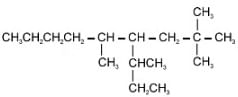 is
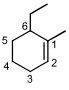
is