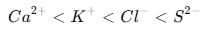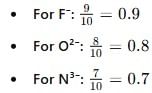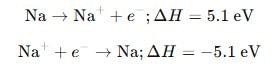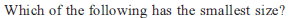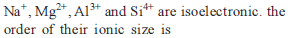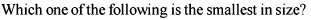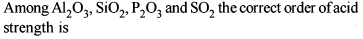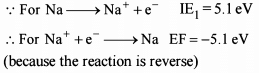Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties - 1 - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties - 1
Which is the correct order of ionic sizes (At. No. : Ce = 58, Sn = 50, Yb = 70 and Lu = 71) [AIEEE-2002]
The reduction in atomic size with increase in atomic number is a characteristic of elements of - [AIEEE-2003]
The atomic numbers of vanadium (V). Chromium (Cr), manganese (Mn) and iron (Fe) respectively 23, 24, 25 and 26. Which one of these may be expected to have the higher second ionization enthalpy ? [AIEEE-2003]
Which one of the following sets of ions represents the collection of isoelectronic species ? [AIEEE-2004]
lanthanoid contraction is caused due to - [AIEEE-2006]
The increasing order of the ionic radii of the given isoelectronic species is:
The increasing order of the ionic radii of the given isoelectronic species is:
Identify the correct order of the size of the following:
Pauling’s electronegativity values for elements are useful in predicting
Amongst the elements with the following electronic configurations, which one of them may have the highest ionisation energy?
The correct order of radii is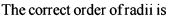
Choose the correct order of the following:
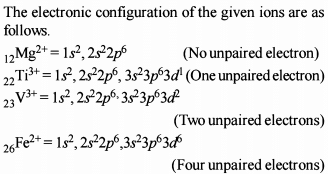
Which has the most stable +2 oxidation state?
What is the value of electron gain enthalpy of Na⁺ if IE₁ of Na = 5.1 eV?
Atomic radii of fluorine and neon in Ångstrom units are respectively given by: