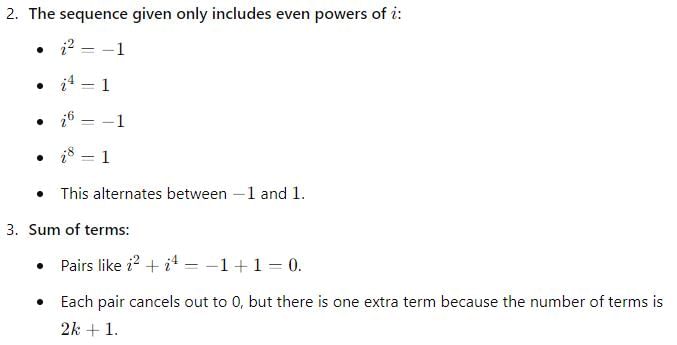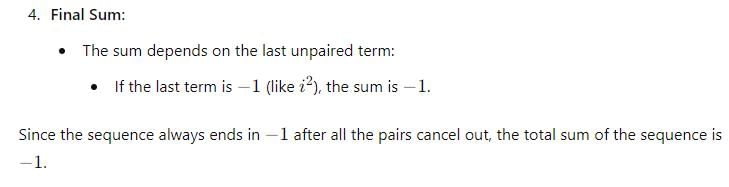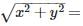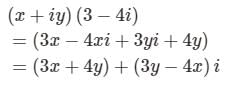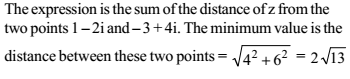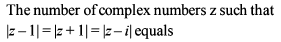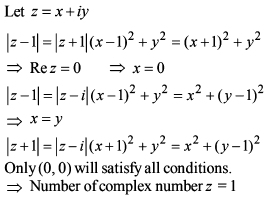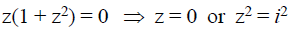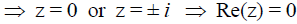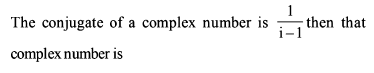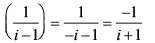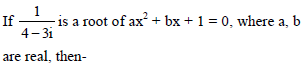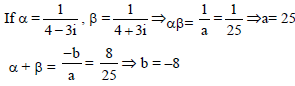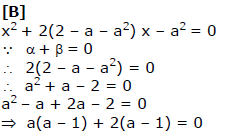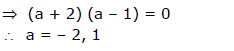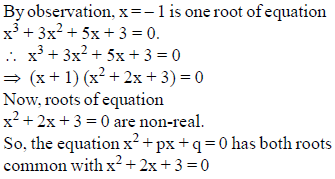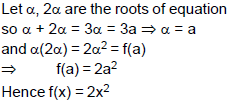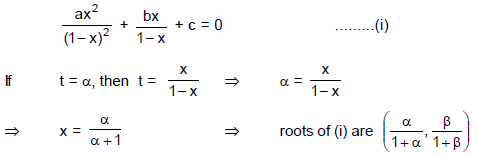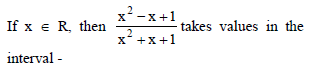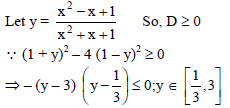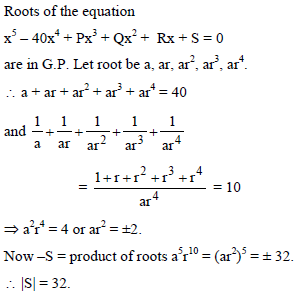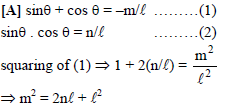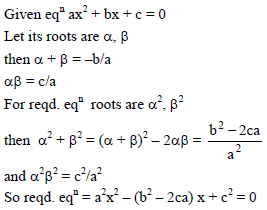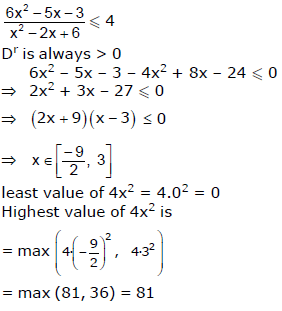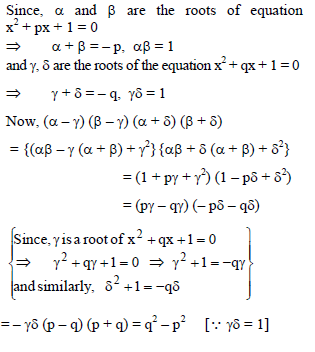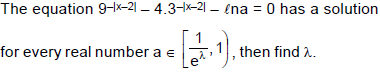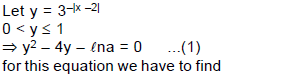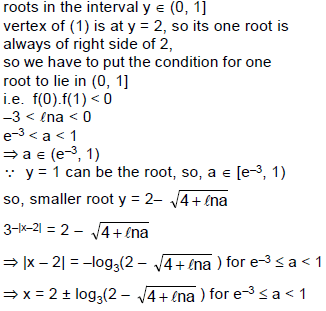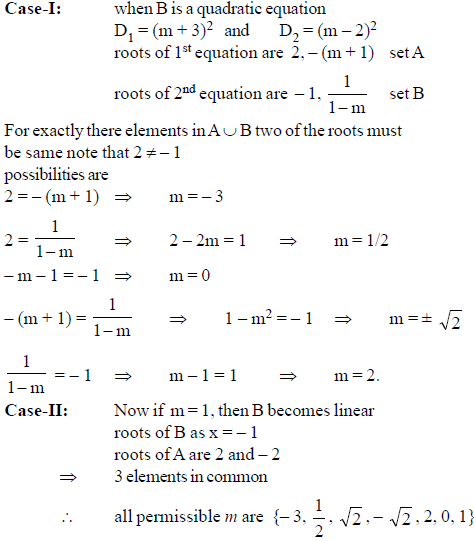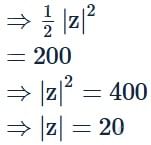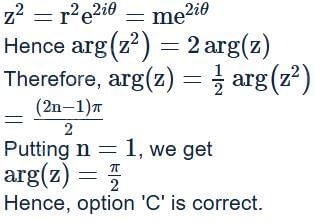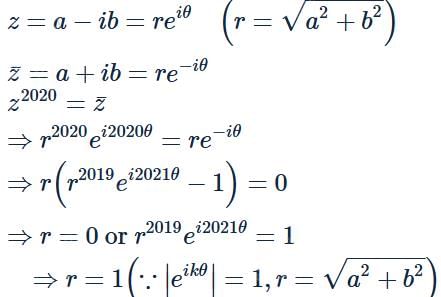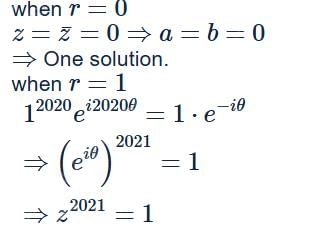Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equation - 1 - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equation - 1
The locus of z which satisfied the inequality log0.3|z –1| > log0.3|z – i| is given by
i2+i4+i6+........... up to 2k + 1 terms, for all k belongs to natural numbers N.
The minimum value of | z – 1 + 2i | + | 4i – 3 – z | is
If z + z3 = 0 then which of the following must be true on the complex plane?
For what value of a the sum of roots of the eqn. x2+ 2 (2 – a – a2)x – a2 = 0 is zero-
If the equations x2 + px + q = 0 (p , q ∈ R) and x3 + 3x2 + 5x + 3 = 0 have two roots common, then find the value of (p + q).
If for all real values of 'a' one root of the equation x2 – 3ax + f(a) = 0 is double of the other, then f(x) is equal to
If α, β are the roots of the equation ax2 + bx + c = 0, then the equation ax2 – bx (x – 1) + c (x – 1)2 = 0 has roots
If the roots of x5 – 40x4 + Px3 + Qx2 + Rx + S = 0 are in G.P. and sum of their reciprocals is 10, then |S| is -
The equation whose roots are the squares of the roots of the equation ax2 + bx + c = 0 is
If α, β are the roots of x2 + px + 1 = 0 and γ, δ are the roots of x2 + qx + 1 = 0, then q2 – p2 is equal to -
Let A = { x | x2 + (m – 1)x – 2(m + 1) = 0, x ∈ R}
B = { x | (m – 1)x2 + mx + 1 = 0, x ∈ R}
Find the number of values of m such that A ∪ B has exactly 3 distinct elements.
If the area of the triangle on the complex plane formed by the points z, iz and z + iz is 200 square units, then |z| is
If k + |k + z2| = |z|2 where k is real, then a possible argument of z is
Number of ordered pairs (a,b) of real numbers such that (a+ib)2020 = a−ib


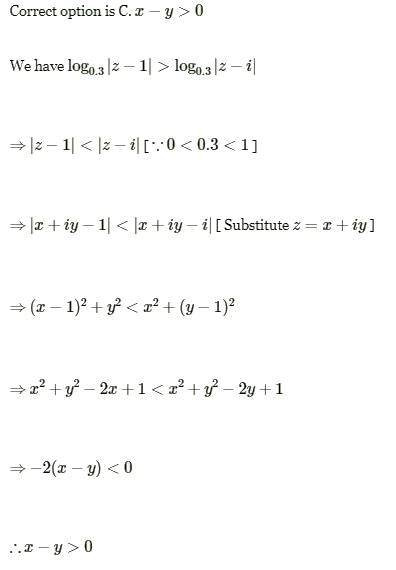 =
=