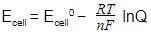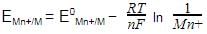Test: Nernst Equation - NEET MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Nernst Equation
Three cell A, B and C has equilibrium constant in the ratio 1:4 : 9 respectively. Arrange the following cells in the order of increasing Gibbs free energy.
Gibbs free energy change for a cell reaction is positive what does it indicates?
Consider the cell reaction:
Cd(s) | Cd2+ (1.0 M) || Cu2+ (1.0 m) | Cu (s)
If we wish to make a cell with more positive voltage using the same substances, we should:
. The electrode potential at any concentration measured with respect to standard hydrogen electrode can be represented by:
. For an equation: Ni(s) + 2Ag+(aq) → Ni2+ (aq) + 2Ag(s) the Nernst equation is written as:
Nernst equation for an electrode is based on the variation of electrode potential of an electrode with:
The free energy change for the following cell reaction is given as :
2Au3+ (aq) + 3Cu (s) → 2Au (s) + 3Cu2+ (aq)