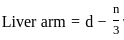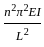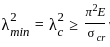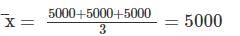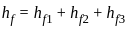HPCL Civil Engineer Mock Test - 1 - HPSC (Haryana) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - HPCL Civil Engineer Mock Test - 1
A candidate who gets 50 percent marks fails by 100 marks but another candidate who got 78 percent marks gets 30 percent more than the passing marks. The maximum marks is:
What quantity of sugar costing Rs 9/kg should be mixed with 27 kg of sugar costing Rs 7/kg so that the shopkeeper can make a profit of 10% by selling the mixture at Rs 9.24/kg?
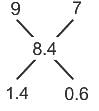
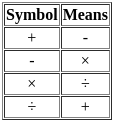
If + means, -, × means /, - means + and / means ×, then find out the answer of the following question :
(48 × 6)/4
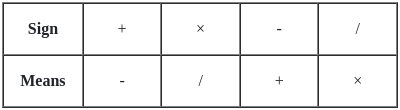
If '+' means '−', '−' means '×' , '×' means '÷' , '÷' means '+', what will come in place of the question mark?
153 × 9 - 5 + 32 ÷ 90 = ?
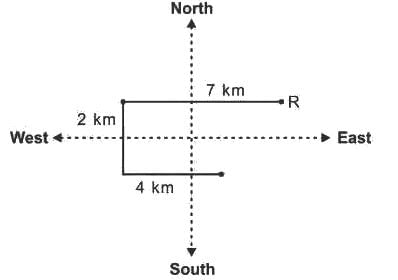
Vikram started from point R and walked straight 7 km west, then turned left and walked 2 km and again turned left and walked straight 4 km. In which direction is he from R?
Select the option that can be used as a one-word substitute for the given group of words.
Someone in love with himself
Choose the word that is opposite in meaning to the given word.
Devious
Directions: In this section, each of the following sentences has a blank space and each sentence is followed by four options. Select the most appropriate option to fill the blank space.
This time next week, they ______ in Canada.
If the sum of 40% of a number and 30% of the same number is 70, then the number is:
A marked price of an article is 20% above than the cost price of an article. A shopkeeper allows a discount of 10%. A selling price of an article is 2160. Find the profit percentage.
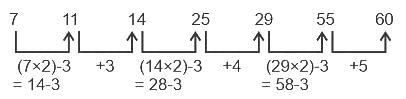
Select the number from among the given options that can replace the question mark (?) in the following series.
7, 11, 14, 25, 29, 55, ?
Direction: In the following question assuming the given statement to be true, find which of the conclusions among given conclusions is/are definitely true and then give your answers accordingly.
Statements: M > N = O < P ≤ Q, R > S ≤ Q
Conclusions:
I. N ≤ S
II. O > S
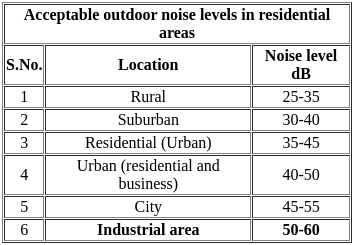
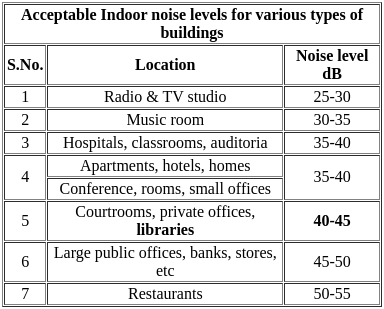
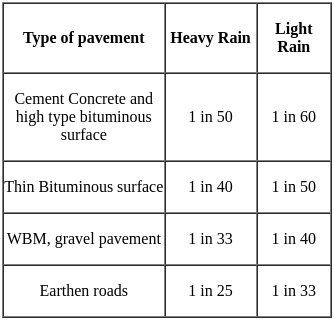
This method of adjusting a traverse is adopted when the angles are measured very accurately, the corrections being applied to lengths only. Thus, only directions of the lines are unchanged and the general shape of the diagram is preserved. This method is known as ______
The amount of irrigation water required to meet the evapotranspiration needs of the crop during the full growth is known as
The relation given by Kennedy for critical velocity Vo (in m/s) is
Where m = critical velocity ratio
D = depth of water in m
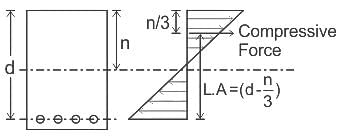
If d and n are the effective depth and depth of the neutral axis respectively of a singly reinforced beam, the lever arm of the beam, is
In highway cross sectional elements, what is the minimum shoulder width recommended by the IRC?
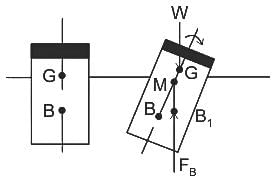
What type of equilibrium depicts from the figure given below?
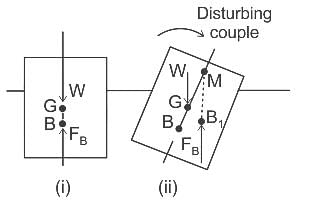
where G = centre of gravity, B = centre of buoyancy, M = Metacentre and B1 = new centre of buoyancy.
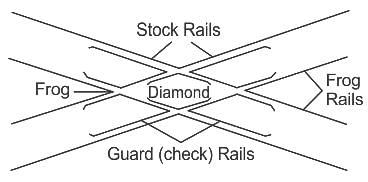
A__________ is meant for transferring a vehicle from one track to another track and vice versa.
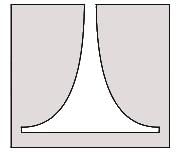
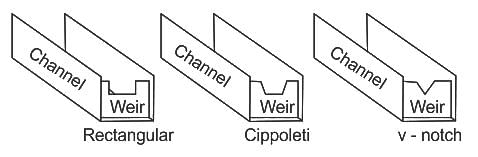
Identify the flow control device shown in image:
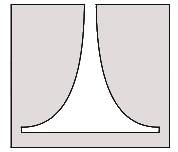
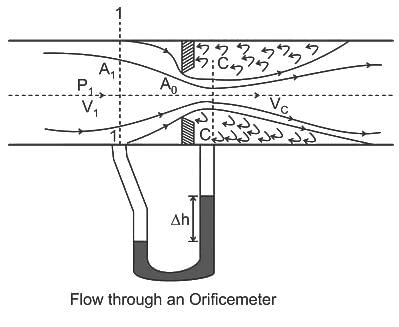
In an orifice the coefficient of contraction is defined as the ratio of
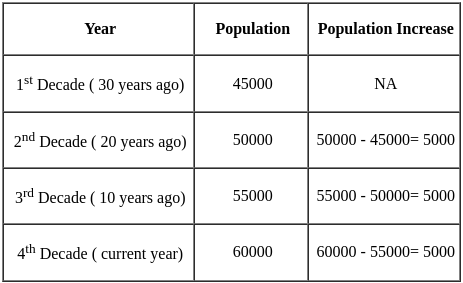
Census records indicate the current population of a city as 60000, population 10 years ago as 55000, population 20 years ago as 50000, population 30 years ago as 45000. What would be the probable population after two decades (20 years), when calculated using arithmetical increase method?
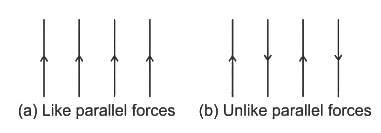
The three forces of 100 N, 200 N and 300 N have their lines of action parallel to each other but act in opposite directions. These forces are known as -
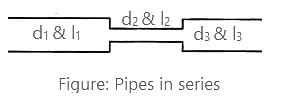
Three pipes having diameter d1, d2 & d3 (d1 > d2 > d3) are connected in series. Identify the correct option pertaining to the flow through the pipes.